Introduction
Any company that trades physical goods deals with freight shipping. Such companies order raw materials, move end products between warehouses, and finally ship products to the customers. Smooth logistics are critical for a functioning business.
Yet, without an automated system, logistics planners waste hours building the routes, doing paperwork, or communicating with the drivers. This is true for both freight forwarding companies and internal logistics departments.
Most companies understand the weak points of their logistic planning, but there are some pitfalls as well. Some companies have outdated ERP systems that end up not helping too much.
Today, we’ll take a look at both manual and automated ways to manage freight shipping. We’ll check the common difficulties of manual route planning, and find out ways to fix them.
Hopefully, the article will help you excel at route planning. You’ll learn how to maximize the number of shipments per employee. Here’s how to make shipments fast, reliable, and with minimum expenses.
The details of planning freight shipping
You can divide freight planning into strategic, business, and operational. Today we’ll look into the latter. This article will not help you decide if you should venture into the Chinese market. Instead, we’ll help you carry out your daily shipments as smoothly as possible.
Let’s take a look at the daily duties of a logistics planner:
(1) Learn the delivery routes. There are endless routes in global logistics. To keep costs low and deliver freight on time, the planning manager should consider:
- Road quality
- Traffic load
- Customs
- Tolls
(2) Check delivery terms. To keep freight in good condition, the planning manager learns the norms and conditions of shipments. Complying with these documents will keep the freight fit, and minimize spoilage.
(3) Select the right vehicle type for the cargo. Different shipments need different trucks. For example, dairy or medicine freight would require a refrigerator. Some shipments would also require oversized trucks, or special vehicles for dangerous goods, etc. Depending on the load, it’s also important to check if there are enough fasteners, fixtures, and other equipment.
(4) Check the permits and other paperwork. The vehicle needs to have a valid technical inspection, insurance, permits for international transport, etc. Drivers themselves should have valid medical permits, a driver’s license, etc.
(5) Without permits and insurance, a company can get huge fines. It’s important to make sure that the paperwork is valid.
(6) Notify the drivers about the work ahead. Without an automated ERP, a shipment planner would have to manually call or text the drivers to let them know about the shipping.
(7) Build the route. The logistics planner will build the route that matches the client’s requirements. Sometimes, the priory is to deliver the freight as fast as possible. In other cases, the goal would be to deliver the freight avoiding extra costs. To find the route that fits best, the logistics planner considers fuel consumption and costs, toll road costs, delivery deadlines, etc.
If the planner builds a poor route, the driver may not meet the deadlines. This can cause the company to lose customers and have large financial penalties.
(7) Avoid empty runs. To choose the closest vehicle, the planners need to see the workload of every vehicle in the fleet. Customers don’t pay for the empty runs, so it’s important to minimize them whenever possible.
(8) Get the documents ready in time. It’s important to send the documents to the cargo manufacturer in time. This way they can release the freight to the drivers without a standstill.
(9) Be flexible. Even the best logistics planner can’t guarantee that the delivery will go as planned. The key is to expect surprises and be ready to adjust the routes on the fly. The more spreadsheets an employee has to handle, the more difficult it becomes to stay flexible.
These are only the high-level tasks of a logistics planner. Freight forwarders have few planners compared to the number of drivers. So logistics planners include all kinds of tasks. Some of them are described in the picture below.
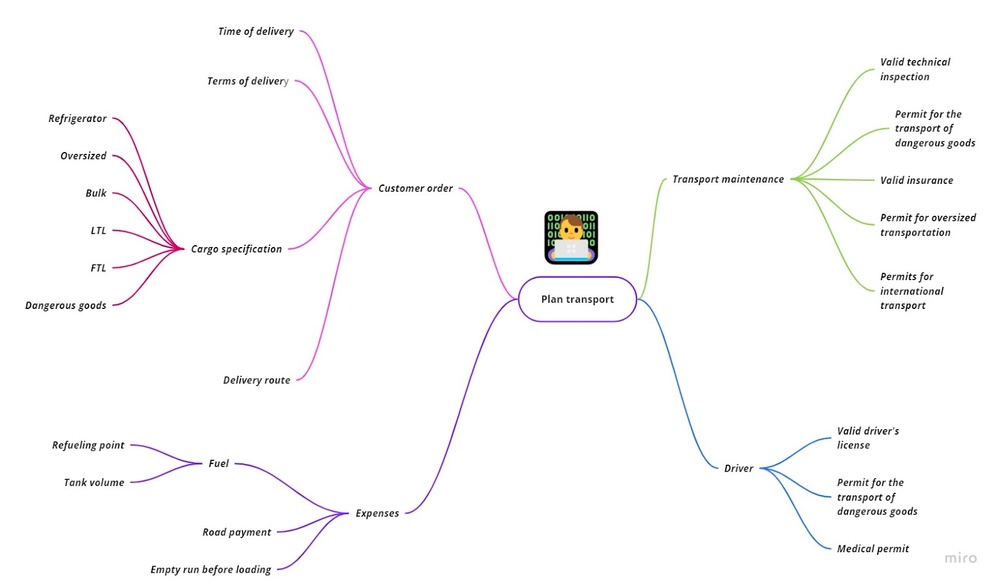
Here’s the main challenge for the planning manager. If the company doesn’t have a system that automates the workflow, the logistics planners can easily get overwhelmed.
The problem is that they have to switch back and forth between several types of software to do their work. This includes accounting, technical service, sales, and transport monitoring systems. On top of that, they have to keep track of huge datasets across multiple Google Sheet or Excel documents.
All of this slows down the employees and causes human error. Naturally, this means extra costs for the company.
What can an automated system do?
Looking at the list of the logistics planner’s tasks in the previous chapter, you may have noticed that a lot can be automated. Indeed, if done right, an ERP will save tons of time and money for a shipping company.
A human-friendly system for planning and adjusting routes would store all the data in one place. This would allow the logistics planner to see the big picture. When the route planners have all the relevant info in front of them, they can make better decisions and be more flexible.
On top of that, they wouldn’t have to pass information back and forth between spreadsheets. A robust system would do it automatically and with no errors or typos.
Many companies have outdated or weak ERP systems. Such systems can handle some data but still require the planners to keep several Excel spreadsheets open at all times.
Let’s see how a good ERP system can help a shipping company. Here’s what it can do:
- Store all the data related to route planning;
- Maintain a database of vehicles and their technical status. All the permits and maintenance statuses should be easily accessible;
- Monitor vehicles via GPS, check their fuel level, and other parameters;
- Keep the drivers database. This will help checking their availability, medical permits, driver’s licenses, and so on;
- Lay the routes. Some ERPs will allow to build a few route options based on the filters like tolls, customs, local fuel prices, and so on. The logistics planners will choose the best option and edit it if necessary;
- Automate mundane tasks, like driver notifications.
How can automation help logistics businesses?
It is difficult to handle large volumes of data. The human brain can only process so much information at once. So the less data a logistics planner has to process, the more efficient they become. Thankfully, software can take care of this issue.
Here’s what it helps with:
Conclusion
With automation, route planning will become faster. On top of that, a good ERP will eliminate human errors which can also be quite costly. All of this reduces logistic expenses.
Finally, with effective route planning a freight forwarder can make more shippings, which means higher profits for the company.
To learn more about the ERP, feel free to reach out. We have 10 years of experience making logistics software, including building an ERP for a logistics company or an ERP for a car shipping company. We’ll be glad to discuss logistics software that would benefit your business.





