Introduction
It’s difficult to secure personal data on the internet. Breaches occasionally happen even to the most secure organizations. The US government, Apple, T-Mobile were all hacked within the last couple of years.
This applies to eLearning as well. Student data from the most prestigious universities like UC Berkeley, University of Central Florida, and Australian National University was exposed.
To minimize such breaches in the US, regulations like FERPA, CIPA, COPPA, and other similar regulations have been enacted. These regulations ensure student privacy and let them learn in a safe and secure environment.
Today we’ll discuss what exactly is PII? Why is it important? What basic laws should elearning platforms comply with? And what security requirements can be employed to secure eLearning platforms?
What is PII?
PII stands for personally identifiable information. Any information that separes you from other people is PII.
In the eLearning world, this could include the learner’s:
- Name
- Address
- Social Security Number (SSN)
- Student StateID
- SIS ID
- Login / Email
- Grades
- Disciplinary records
- Any other indentifieble information
Why Do We Need To Secure Students’ PII?
The value of PII cannot be underestimated, as it can be vital to a person’s identity. Without proper protection of students, many privacy concerns would become worrying, including data privacy, personal privacy, information security, etc.
A lack of adequate protection exposes all of the above and more to data thieves and individuals with malicious intent. They can use this information to create false accounts, perform unsavory online actions, and commit identity theft and related crimes. Protecting the PII is a priority, and laws are made just for this purpose.
This type of information is protected by federal laws and regulations, like FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act), CIPA (Children’s Internet Protection Act), and COPPA (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act).
PII covers all information that can be used to identify and differentiate one person from another. With such data hackers can identify anonymous people and reveal vital information about them. This includes students, applicants, faculty members, etc.
What is FERPA?
FERPA stands for Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act. Enacted in 1974, it is a federal legislation that limits how public entities can access educational information and records. This includes future employers, publicly financed educational institutions, and foreign governments.
Basically, FERPA is a law that applies to all educational institutions that receive funding from the U.S. Department of Education. It gives students and parents certain rights regarding the privacy of their academic records. This includes the right to access and review their records, request that their records be amended, and even the right to file a complaint when their rights have been violated.
FERPA has two primary purposes. First, it allows parents and students above 18 permission to access information in the student’s education record. Second, it prevents third parties from gaining access to this information without explicit consent from parents.
Want to know what schools does FERPA apply to? The answer is that it applies to any school that receives financing from the government in any way. This covers all public schools and even most private institutions.
According to FERPA, students generally do not have access to their records until they they turn 18. At that point, they are referred to as “eligible students.”
What is CIPA?
CIPA stands for Children’s Internet Protection Act. Its primary concern is to limit children’s access to online adult content.
CIPA deals with internet safety in schools and libraries. It applies to all K-12 schools and libraries that receive federal discounts for internet access. To receive E-Rate discounts, CIPA requires schools and libraries to have internet safety policies.
Educational institutions must block obscene and potentially hazardous content on the internet. They also need to monitor online activity of students. On top of that, they’ve got to publish their compliance practices and hold at least one open meeting to prove that they are following the rules.
What is COPPA?
COPPA stands for Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act, and it was an act enacted in 1998. It falls within the ambit of the Federal Trade Commission.
The act focuses on websites, platforms, and online services that collect personal information from children below 13 years.
Essentially, COPPA regulations ensure that parents are notified, and expressed their permission to collected about a child. Whatever the platform or website, it must have a clear privacy policy and the capacity to secure the data of its users properly.
As to who COPPA applies to, websites and applications that can be accessed by children below 13 have to comply with COPPA. As a result, this will also cover schools with e-learning platforms and websites for their students, especially for K-12 systems.
In situations where the entire purpose of the platform or website is purely educational, the FTC allows schools to stand in for parents. As a guide, schools must observe due diligence in their vetting process for products and services made available for their students and give such necessary information to the parents.
Why should learning platforms comply with these regulations?
Well, noncompliance can result in some pretty hefty fines and penalties. But more importantly, compliance is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of students, parents, and other stakeholders. When personal information is mishandled or exposed, it can cause serious harm to individuals and damage an educational institution’s reputation.
What steps could be taken to protect PII?
So, how can we ensure eLearning software complies with these regulations? Here are a few steps developers and educators can take:
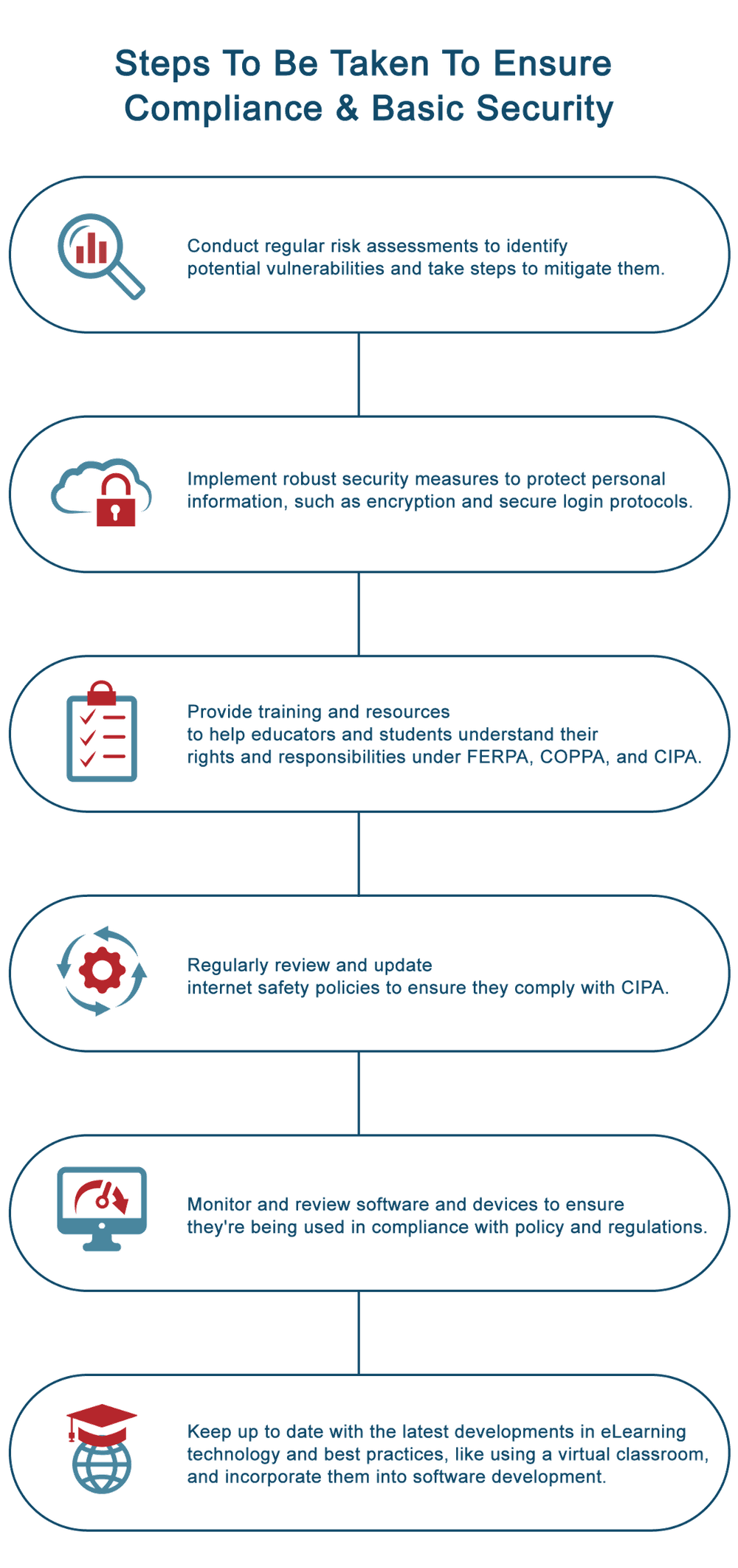
- Take basic security measures. Use HTTPS encryption and secure authentication protocols like OAuth 2.0, LDAP, or others.
- Don’t collect PII whenever you can get along without it. The less private data you handle, the fewer breaches can potentially occur. For example, some K-12 EdTech platforms can habitually store student grade levels even though they don’t need to. Remember: less is more.
- Anonymize data when possible. For example, when you create utilisation & performance reviews, you should anonymize most of the data for it.
- Discard unused data. If your software cycle lasts for just a year, don’t keep the PII afterwards. You can always anonymise this data if you need it for analytics.
- Check vulnerabilities in the vendor libraries that you use. Use external services like Snyk or OWASP projects before every deployment.
- Isolate PII from other data. Encrypt all PII at rest, and use internal identifiers in your system.
- Secure your backups. A common mistake is to secure and encrypt current data, while still leaving backups vulnerable.
- Always comply with OWASP standards during development. Design your system to comply with at least OWASP Level 1 at all times, although Level 2 is recommended.
- Audit your system regularly to ensure that the development hasn’t brought on new vulnerabilities.
By taking these steps, we can secure personal information. Remember that security is a continuous process, so it’s essential to regularly review, update, and implement new measures to keep PII away from hackers.
Conclusion
Safeguarding the data and information of students is a vital part of data protection, one that parents, schools, and other concerned institutions must take seriously. The modern technological shift requires that existing regulations be appropriately interpreted and applied, and e-learning platforms should be at the forefront.
Aristek provides many services, including building e-learning platforms that comply with the existing regulations while meeting the needs of users. An excellent example of this is our K-12 elearning platform for a satisfied client. Do well to contact us right away!




