Summary
In this article, we spoke with our CCO, Ruslan Makarsky, who is an expert in custom educational software development and has a deep understanding of the K-12 industry.
We have discussed the challenges that publishers face while delivering their content to K-12 LMSs and the ways they can be addressed.
Here is what we were able to find out.
A strong educational foundation is the key to unleashing a child’s potential. The K-12 industry plays a vital role in shaping the minds of future generations.
Developing truly worthwhile custom EdTech software solutions is no walk in the park, but we’re pulling out all the stops.
When it comes to educating future generations, I don’t believe in a one-size-fits-all approach. Accessible education is what we will go the extra mile for.
Artificial intelligence is a game-changer for elearning, enabling personalized and adaptive experiences that cater to the unique needs of each learner.
7 Questions & Answers
1. What Problems Do HE (Higher Education) Institutions Content Publishers Experience When Using LMS Systems to Deliver Their AG or Other Content to K-12 Schools?
There are several areas of concern in the transitioning of curriculum from HE to a Publisher within the K12 market.
Curriculum Content Creation and Distribution
First of all, LMS systems do not allow other LMS systems to access their content interactively. For example, Canvas (HE / K-12) can’t share its content with Schoology (K-12) or vice versa. These and other solutions allow content to be shared with them, but not for them to share out themselves.
LMSs are not publishers of online curriculum products. Their role is to organize and distribute pre-existing curricula or curricula created by the K-12 / HE institution where the LMS is installed.
Another issue with using any LMS for publishing curriculum in K-12 is the lack of or inconsistent data commonly required for licensing and reporting.
Student Grade Level
Note: Some LMS developers will answer yes, but a more profound discovery will find issues such as the field, Anticipated date of graduation, which is not a required field, and sporadically provided, if at all.
There are different issues depending on the LMS implemented. Some of them simply do not provide a Grade Level field. It reminds me of the famous Y2K update. It’s so simple. Why not just give the client what they need?
School Identification
The default configuration for most LMS systems ignores the establishment of schools. This is problematic when generating reports and sharing content with publishers.
Standards Alignment
Reasonably, K-12 states and institutions expect curriculum materials and assessments to be aligned with national or state standards. Standards are currently the most valuable source of information for understanding student performance and accountability at the district, school, teacher, student, and parent levels.
Yet, standards alignment data is often not supported or provided. HE and K-12 LMS systems do not support or facilitate well-standardized alignment of materials and reporting. Therefore, the content you share from an LMS with an e-learning platform will have limited or no capability of facilitating this.
Also the requirement to handle national and state standards for the different curriculum areas in which standards are required, for most publishers is problematic. It would be unusual if this were provided in any LMS currently.
Some LMS systems use tags to identify standards. This is typically not a functional fix for several reasons.
If an LMS does not provide a standards database that can be loaded with the appropriate standards for a state, it will require individual standards to be assigned to materials that must be entered or pasted into a tag rather than being a resource that can be used through a pulldown.
Using tags for standards by an LMS also requires an e-learning platform that provides a standards database to receive and use this information, which will need customization to the content integration process.
While on the subject of standards, this is much more complicated than it seems.
There are commercial solutions that vary greatly in cost, significantly providing the national and state standards services:
- National and state standards database;
- International standards;
- Crosswalk from one state to another’s standards.
There is also a free, open-standards database service, but as of this writing, it is only a partial, inconsistently maintained service. It is helpful if the states you wish to market exist in this database.
However, as a publisher selling a product, you want to go into every new school year with the latest standards required by each state. States change standards frequently, and if your product services all 50 states, in three different curricula areas, and every grade level, it is essential to understand how this can be best facilitated.
Important note: Changes in standards always require modifications to your content. It’s just a matter of how many per material and assessment. To assist the curriculum writers, your platform should have tools that simplify this task. Some changes actually require the sentence structure to be modified.
2. What Features Should Higher Ed Institutions Publishers Look for When Choosing LMS to Deliver Their AG or Other Content to K-12?
There are many more factors to consider. It requires a deep understanding of all the factors above and more to adequately evaluate the best solution for your needs.
K-12 content capabilities required in an e-learning platform
In K-12, a publisher’s platform must provide content sharing within many different custom LMS solutions. For example, Canvas, Schoology, Google Classroom, Infinite Campus, and others.
Many align with 1EdTech’s LTI content-sharing protocols. However, Google Classroom has its own proprietary requirements, as do others. For example, there are also other LMS systems, such as Blender, that are required by large districts in FL. Regardless, most LMSs harbor their own set of unique nuances you must account for in the different content-sharing capabilities to function appropriately.
Within the LMS solutions above and others, K-12 institutions expect content and assessment-sharing features, such as Deep Linking and Grade Pass Back.
Some LMS systems do not support LTI 1.3 grade pass back. They may say they do, but they do not: ThinCC, QTI and others, depending on the district.
Google Classroom (Proprietary): Curriculum Materials and Assessments and Grade Pass Back
The short of it is this: LMS systems do not facilitate many of the features or requirements needed within the K-12 market.
Localization & Translation
A highly desired and often required functionality is providing materials in other languages. In the United States, Spanish is a common request by K12 clients. Supporting a wide range of languages is a great selling point and notably increases your TAM. Translating materials into other languages is costly, time-consuming, and continual.
WCAG: Accessibility
The requirement for WCAG A – AA levels has increased significantly in the last five years. It is written into many RFPs, especially by larger K-12 institutions. This can not be ignored, as it has been in the past.
Takeaways: Some limitations are more problematic than others, but they are all significant hurdles to adoption in K-12 if they are not provided.
To become a publisher in K-12, you need an e-learning platform that can meet the requirements of K-12. LMS solutions are unable to meet this requirement at all or well.
K-12 onboarding requirements (Content, SSO, Data Integration)
Another major hurdle is the K12 onboarding requirements. They are essential in facilitating an automated process for provisioning K12 clients that significantly reduces client support and facilitates client acquisition and retention.
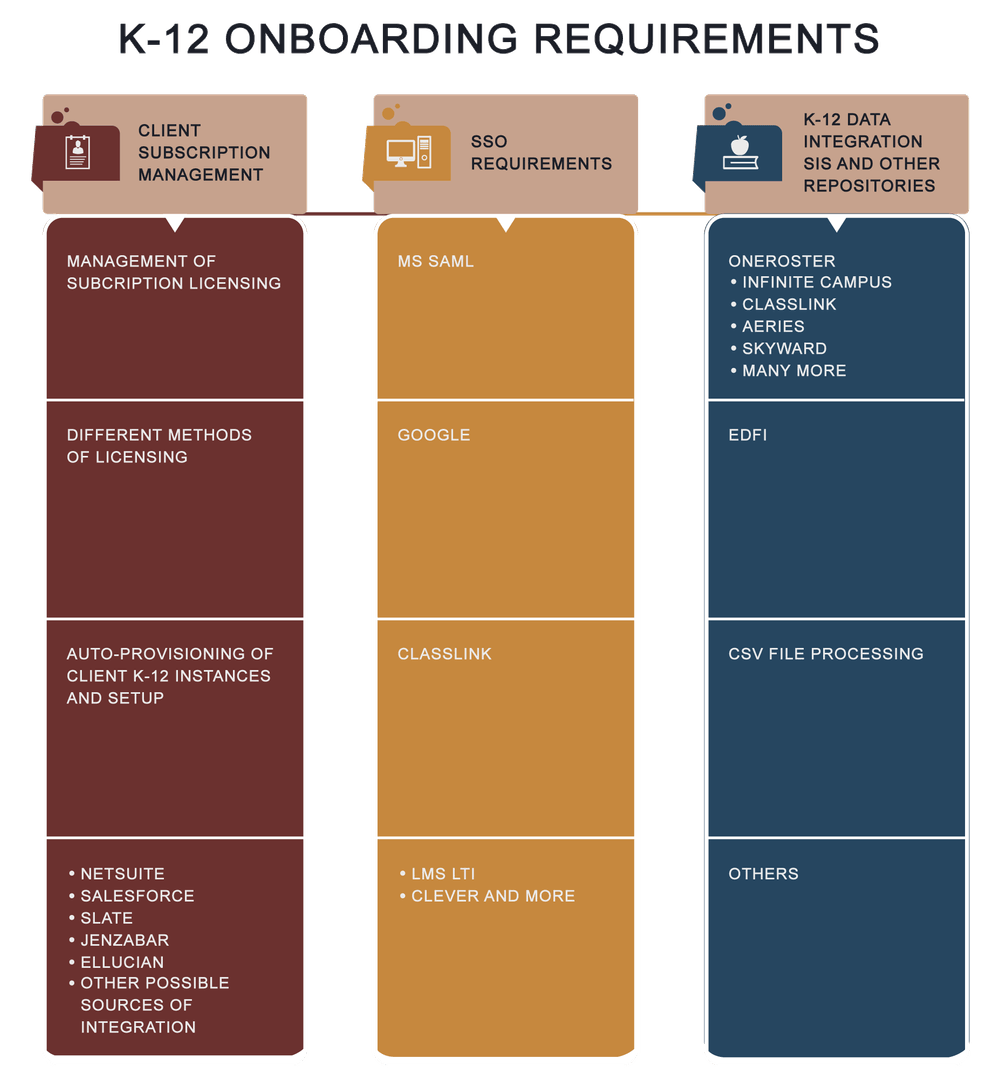
The methods above facilitate the data integration of the following areas: District, School, Staff, Students, Teachers, Sections and Enrollment.
What is expected of such K-12 data integration is the automatic, continual loading and maintenance of the staff, students, course, and course enrollment information, regardless of the source(s) and how many are required. A solution must handle the simultaneous processing of data integrations across all clients for as many different integrations as a client may have.
In addition to the specific nuances each SIS integration repository presents the protocol to be used, there are requirements districts expect to tailor their data integration and the platform itself to meet their specific needs.
These are options such as facilitating non-standards grade levels, easily activating or inactivating teachers, students, and course enrollment, and many others that are an extra measure of meeting client needs. I call these crowd pleasers.
Central Management
A publisher should provide central management at the Publisher and the Publisher client levels to facilitate all of the above and more.
At the client level, having a Customer Implementation Management Console is key. Here is where the publisher and the client’s implementation support staff manage their specific requirements:
- SSO Console;
- Simultaneous Data Integration Repositories and Proprietary CSV File Integration Setup;
- Integration journal;
- Staff, Student, Sections, Enrollment;
- Facilitate simultaneous integrations with unique EdTech TAM and sales, increasing controls and options across all data sources and protocols;
- Integration data access, error, and warning identification;
- Client implementation wizard and progress tracking;
- Platform admin, teacher, and student access credentials notification;
- User password reset options;
- KPI analytics acquisition and reporting;
- Resource / LMS endpoint management.
Such visibility provides for a quick understanding of issues that arise and accountability. This is important during high volume periods in K-12 such as the start of the school year.
Important Data Integration Consideration
There are data integration services that are popular with K12 institutions but not publishers. These services require publishers (including HE institutions publishing into K12) to pay a fee to use their SIS integration services, which the publisher’s clients do not pay.
In the recent past, Clever and PowerSchool are examples of such data integration services that provide data and SSO integration only. They do not offer LMS content-sharing services. These vendors charge publishers, and not the publisher’s clients, for this service.
Their fees are not trivial and will increase the cost of a product, which must be passed on to the client if a publisher wishes to meet its net margin goal. In most cases, the client only understands the effect of this arrangement if you explain it to them.
Publishers must also consider future ramifications. If a vendor implements such a paid integration service, it will be challenging to remove clients from such a service at some point in the future. The situation above could quickly happen if a paid integration service provider decided to increase their fees in the future.
An interesting point to make here is that the ability to provide clients with a simple CSV file format to use for onboarding is a requirement to maximize your TAM. From our experience, a large number of clients still require this functionality in the publisher platforms we have produced.
It is also an important option to offer clients as an alternative. If you do not provide CSV data integration, you are not providing yourself with an alternative for your K12 clients to use rather than using a paid-for data integration service like Clever and PowerSchool mentioned earlier.
An old rule in business is still valid today: never let anyone get between you and your client. Above is an excellent example of why.
I have been charged with facilitating the means to avoid purchasing such publisher-paid integration services to avoid increasing prices or reducing margins, and have been able to achieve this objective successfully.
Every organization has different expectations and needs. However, the above challenges and more need to be reviewed to understand what elements are needed to meet the requirements of your targeted clients and maximize your product’s TAM.
3. What existing LMS systems are currently used to deliver content from HE institutions to K-12 schools?
Online K-12 publishers often use self-created platforms to create curriculum content materials and assessments. For example, Houghton-Mifflin, McGraw-Hill, Pearson, and others.
Publishers share their content with LMS systems through standard protocols and those of non-standard, such as Google Classroom integration. Some LMSs can export its content into a Scorm or Common Cartridge format. In such cases, it must be loaded into a platform that supports such content formats along with the other K-12 institution requirements of Content, SSO, and Data Integration.
The publisher’s platform must be able to load the content from the provided format and fit it into the curriculum mapping (sequence) and structure provided within its framework. Meaning at a high level of functionality, there is a teacher’s suite where the teacher can view their sections and students and assign them homework, tests, view results, etc. There must also be a student suite where students can access their assignments, take their tests, see their results, etc.
These are essential requirements, but the functionality and features provided, along with the ability for customization, are a crucial difference between all solutions. The point is that a publisher’s platform where your HE content will be delivered must have functionality within itself before sharing its content with one or several different LMS systems used within a K-12 institution.
Even if an LMS could accept SCORM or Common Cartridge content file export formats and they could be ingested into another LMS (which is not a straight conversion), it would be deficient in handling just the basic expectations of K-12 institutions.
4. What major changes in K-12 education are expected in the coming years, and how can these changes affect content providers (HE institutions)?
The requirements by K-12 will only increase in the area of content sharing capabilities. Institutions looking to leverage the K-12 EdTech market for enrollment or AG courses know they will need to move to a publishing environment that can address the needs of K-12 institutions and move away from LMS solutions to meet K-12 needs.
There are additional items that HE has to address as well.
Working With State Departments
Many publishers have an objective to become a core curriculum, so they may be included and become part of state adoptions. The requirements for a successful bid for adoption vary by state, but to be one of the choices selected in an adoption is better than not being one.
However, some important mechanics come into play with being selected.
You will be expected to integrate into a state’s Textbook Repository system through an API. These systems were initially created to purchase and distribute textbooks and have kept the same name even though they also accommodate online curriculum subscriptions. This API varies between states.
These APIs are in place to understand what districts will purchase from an approved vendor. The subscription manager we mentioned earlier must align with these state systems.
It is important to note that your licensing, such as District Wide or School Level, Curriculum Area, and Grade Level, will be selected from the state’s order system provided to districts and then forwarded to your system for processing.
On the other hand, it is possible that you would receive orders from districts/schools, and you would have to communicate this to the state system applicable public school orders from their state. In addition, you must use their API in some states to receive funds, or you do not!
As a publisher moves towards the state adoption level, they often start to provide materials expected from a core curriculum, such as student handbooks, teacher guides, kits, and more.
The mentioned state APIs will handle online, print, and kit products and bundles comprising a combination of the product areas. Often, such physical materials must be sent to a state textbook warehouse, where the state distributes the district orders to the appropriate district warehouse.
Some have implemented the ASC X12 EDI (Accredited Standards Committee X12, Electronic Data Interchange) to coordinate the procurement, change orders, cancellations, corrections, and distribution of large inventory volumes.
5. How major problems in content delivery processes can be addressed?
The Good News
To become a publisher in K-12, you essentially need an eLearning platform that can meet the requirements of K-12. LMS solutions were not created to meet the previously mentioned requirements and others that were not.
LMSs have been adopted mainly because there are few Buy platform options in the Buy vs. Build equation. eLearning Integration Tool provides an eLearning platform that allows an organization to create their online product much quicker and for much less money, resulting in a more mature solution.
The eLearning Integration Tool Learning Platform Quick Review
eLearning Integration Tool is a unique EdTech platform that supports K-12, Professional Development, Higher Education, and consumers at the same time.
Important to note are the critical hurdles discussed in the first and second questions. K12 publisher’s client requirements are considerably broader and more involved than any LMS can facilitate well in total or partially. The eLearning Integration Tool K12 platform provides solutions to these deficits and issues.
The Solution to Content Challenges, Additional Added Value & Protections
Almost all mainstream HE LMS systems provide the means to export their content in SCORM, and a few in Common Cartridge format.
The eLearning Integration Tool platform can load these exported files through its curriculum authoring tools while providing mirrored functionality of the original content, curriculum structure, and functionality required by K-12 institutions. This eliminates the problem of maintaining the curriculum on two different platforms.
In addition to this, eLearning Integration Tool provides version control as well. An advantage is the ability to customize the platform to automate the process mentioned above if desired. eLearning Integration Tool also provides a content structure to organize the materials when loaded that can be controlled and aligns with the existing Teacher and Student Suites.
This imported curriculum content and assessments facilitate the K-12 institution’s content-sharing requirements within their own LMS(s) of deep linking, grade pass-back, and others.
At some point, eLearning Integration Tool might be the preferred primary owner of the content as it provides more robust assessment types than are found in many LMS systems, version control, all onboarding requirements for K-12 / HE / Consumer, subscription management, and more.
For example, eLearning Integration Tool can be customized to provide state test assessment item types to match closely those students would see on an online state test if desired.
We created the means by which to control LMS systems. For example, we can assign and remove materials/ assessments under the platform’s complete control. This is useful in benchmark testing, curriculum mapping required assignments, etc.
We created the ability to protect and limit access to content within an LMS or any other external solution, regardless of the format implemented.
The Solution to Onboarding Challenges
eLearning Integration Tool provides an inherent architecture designed to facilitate all the needs of K-12 institutions at all levels.
One significant deficit of LMS solutions is their lack of supporting essential data needed for licensing and required reporting. In eLearning Integration Tool, it supports this data with ready-to-use reporting. Below is a recap of the LMS limitations that eLearning Integration Tool remedies.
Student records have:
- Grade Level identified;
- District and attending School location(s) specified;
- District and School State identification codes.
Curriculum materials and assessments are:
- Marked with the appropriate Grade Level(s);
- Curriculum area;
- Standards alignment within materials and assessments.
These fields and their data comprise the structure required to provide the foundation of all reporting in K-12 Institutions.
In addition, there is likely no mechanism for loading or the continual updating of all state and national standards for curriculum areas and their grade levels.
Further, the ability to prove the crosswalk from one standard to another is not provided.
The above features may be integrated into the eLearning Integration Tool platform and your
content, providing a highly efficient means of managing the realm of standards management.
LMS & SIS Integration Tool provides for OneRoster data integration. OneRoster is a standardized industry protocol to exchange teacher, student, course, course enrollment, and other data. This protocol may be processed by CSV files or through a REST API.
Important Point: Each SIS and other repositories that use OneRoster have different nuances that require some work to make them compliant. As a publisher, you must also be certified compliant with the data repositories you facilitate data integration with, such as Infinite Campus, Classlink, and others.
eLearning Integration Tool’s engineers have a deep understanding of these processes, procedures, and contacts to obtain these certifications.
eLearning Integration Tool also provides a tiered structure with the Publisher at the top tier and every Publisher client (K-12 Institution) comprising the next level below. eLearning Integration Tool to provides several essential features of the system.
Subscription Management
- Automated client instance creation;
- Automated license controls;
- Client implementation wizard and progress tracking;
- Platform admin, teacher, and student access credentials notification;
- User password reset options;
- Client implementation and product support measures.
Client Instance Management
- Simplifies business continuity measures of security, scaling, and much more;
- No shared resources;
- Privatized, secure onboarding;
- And more.
SSO
- MS SAML;
- LTI;
- Google;
- Clever;
- and others.
Data Repositories
- Classlink;
- Infinite Campus;
- Skyward;
- and many more.
Data
- District;
- School;
- Staff;
- Teacher;
- Students;
- Courses;
- Course enrollment;
- more.
Client Content Sharing Into Their LMS
Google Classroom
Content Management
Support analytics data collection, warehousing, and reporting at the Publisher and client instance levels.
Publishers are provided personas of super admin, content managers\writers, implementation support, and customer support. Each has its own specific access to appropriate applications and data with system control journaling.
Client personas are site admins, district admins, school admins, teachers, and students. Each has its own specific access to appropriate applications and data with system control journaling.
eLearning Integration Tool has been designed to facilitate external resources within its platform, such as Lexile, Dictionary, TTS, and other external platforms.
The reality of almost all projects is that some product-specific needs require engineering work. Still, it is far less costly and faster than designing and building a platform from scratch.
EdTech Business Process Solution Experience
We have considerable experience in the “business processes” of EdTech.
A high-level look at state adoptions and applicable state department APIs for receiving orders and funds was mentioned early. We have integrated the API’s for Textbook Repository and the X12 protocol to create automated solutions integrated into Salesforce, NetSuite, and Order Management Systems.
We have provided publishers with automated solutions to process print and kit orders to vendors integrated into their SAP, X12, and other proprietary management systems. These solutions monitored all orders for anomalies while tracking order processing, logistics of shipping, and carrier delivery status. This included integrations in Salesforce, NetSuite, and Order Management Systems.
We have considerable experience in Q/A measures of creating content that:
Localization / Translation
We have engineered systems that are still used today to translate curriculum materials. This has many assistive technologies that assist translators, but it still requires human effort.
In recent years, however, we have conducted focus groups that included this topic as to its importance and if our proposed new methods of supporting this requirement and its results met educators’ expectations.
The response was it is a necessary functionality, and yes, the materials were suitable that were created.
We have created a methodology that can be implemented and will maintain itself. The costs are reduced to that of engineering work of integration with your content and support a wide range of languages.
WCAG – Accessibility
The standard requirement for WCAG is to meet levels A – AA levels.
We utilize two of the Accessibility Automated WCAG Certification solutions in the industry. We have also implemented this as a continuous integration process in content workflows.
Most people do not understand that these certifications only cover around 28-30% of the actual WCAG A – AA levels. This, however, appears to be enough currently to satisfy this requirement, but it may not be in the future.
If your application requires a comprehensive alignment with the remaining 70% of the items, you must hire a service to perform manual testing. There are not many of these services. They are expensive and take time, rightfully so for the amount of effort required.
Regarding images and videos, you must cover all manual testing items within this area. All images and videos must support alt-text of the context and what is displayed. To provide the correct functionality, it does not exist, and we engineer a solution that supports this, as this is one area that is scrutinized heavily.
Business Continuity
We have experience in all aspects of business continuity to the highest utilization levels and know how to cost-effectively phase in the appropriate measures at the appropriate time in a product’s progression. From horizontal scalability, holistic client / business operations disaster recovery measures, national\global content caching, cyber security measures and procedures, meeting federal / state security requirements, and more.
Takeaways: To become a publisher in K-12, you need an eLearning platform that can meet the requirements of K-12. LMS solutions are unable to meet this requirement well or at all.
The eLearning Integration Tool platform is a Buy option to utilize in total, in part, or to create your own platform. In all situations, it significantly reduces time to market for much less capital while resulting in a much more mature solution.
6. What technologies are used to create and deliver content to K-12 training from LMS systems used by HE institutions?
SCORM and Common Core
However, we have created unique engineering capabilities to provide functionality in content sharing and the protection of publisher content that is shared. Below is a brief description of these.
eLearning Integration Tool can be customized to provide state test assessment item types to match closely those students would see on an online state test if desired.
We created the means by which to control LMS systems. For example, we can assign and remove materials \ assessments under the platform’s complete control.
This is useful in benchmark testing, curriculum mapping, required assignments, etc.
We created the ability to protect and limit access to content within an LMS or any other external solution, regardless of the content sharing format implemented.
7. What resources and support should be provided to content publishers when working with the eLearning Integration Tool Platform?
LMS & SIS Integration Tool is supported by highly experienced EdTech solution architects, engineers, cloud engineers, implementation support, data scientists (AI/ ML), and advisory services.
Conclusion
We hope all the information provided was useful for you. Yet, if you want to contact our experts for further details or are interested in having eLearning Integration Tool, reach out. We are happy to discuss all the questions you may have.