When you’re building logistics software, you’ll need to choose your mapping platform. But which one do you need? As a user, you come across Google or Apple Maps. But sometimes other options fit better.
This article will help you find the right maps. We’re speaking from experience: we’ve built applications with various maps, and today we’ll share our knowledge with you.
Most popular mapping platforms
Google Maps Platform
Google Maps is the world’s most popular map. They have over a billion monthly users. Also, 5 million apps and websites use it weekly.
With Google Maps you get satellite images, street view, and real-time traffic data powered by billions of Android phones.
OpenStreetMap
OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a free mapping platform where users contribute and maintain map data. OSM is mostly supported by volunteers, so the data may not be as precise.
Compared to commercial maps, there are fewer available features. There’s no traffic data, business listings are not always up-to-date, and the routing is less robust compared to competitors.
Mapbox
Mapbox is a commercial mapping platform based on OpenStreetMap. It takes the best out of OSM and enhances it with commercial data. Mapbox adds live-traffic information, real-time updates, customization options, and more features.
Companies like Wolt, Coupang, and DPD use Mapbox maps.
TomTom
TomTom is another popular mapping platform. Uber uses TomTom’s maps and traffic data. It’s also used for in-vehicle navigation by Mercedes trucks, Volkswagen, and Nissan.
It’s great for smaller logistics companies with <1000 vehicles in the fleet. The platform has ready-made layers for fleet management, routing, traffic, and geofencing. The ready-made layers make development cheaper because you don’t have to reinvent the wheel.
For enterprise software, it’s not such a great choice. Companies with a few thousand vehicles go the extra mile to optimize their business processes. But TomTom’s API is not customizable, so you’ll have to stick with the premade layers.

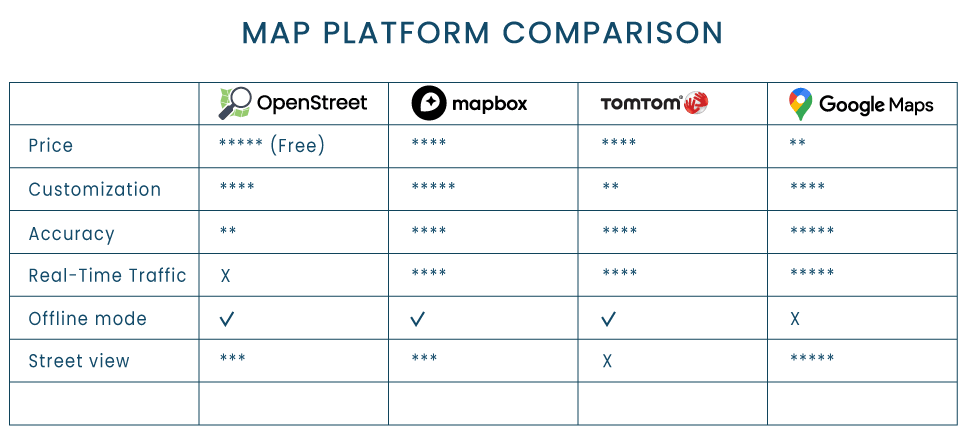
OpenStreetMap is completely free, so it technically wins this round. The caveat is that OSM lacks many basic features that large enterprises can’t go without. Meanwhile, smaller companies can take advantage of the freemium options that commercial maps have.
Comparing the pricing is tricky because the map companies have different pricing models. For example, with Google Maps, and TomTom you only pay for API requests. With Mapbox you also need to pay for the active users, as well as the API requests.
Overall, Google Maps is the most expensive option. TomTom and Mapbox are more comparable, but MapBox is generally cheaper. You can compare some of the prices below.
Note that this table is oversimplified. Map services offer tens of different APIs, each adding up to the total sum. To estimate the total price for your project, check out the pricing pages directly: Google Maps, TomTom, and Mapbox.
You can also reach out to our experts for a free consultation. They’ll help you find the cheapest map provider for your project.

Real-time traffic
Google Maps wins this round. It’s the world’s biggest map service that covers maps and driving directions almost everywhere in the world, from the US to North Korea. It also covers real time traffic data in most countries.
TomTom is also very accurate in the US and Europe. In other regions, like Asia, Africa, or Australia there’s no traffic or speed camera data.
MapBox covers traffic data in the regions below. If you need to know traffic in other countries, choose Google Maps:
- North America;
- Western Europe;
- Middle East;
- Australia & New Zealand;
- Japan & Korea.
OpenStreetMap doesn’t provide live data out of the box. Some companies provide traffic tools for OSM, but these are generally not as extensive as commercial maps.
Custom layers
To optimize deliveries, logistic maps go above and beyond regular maps.
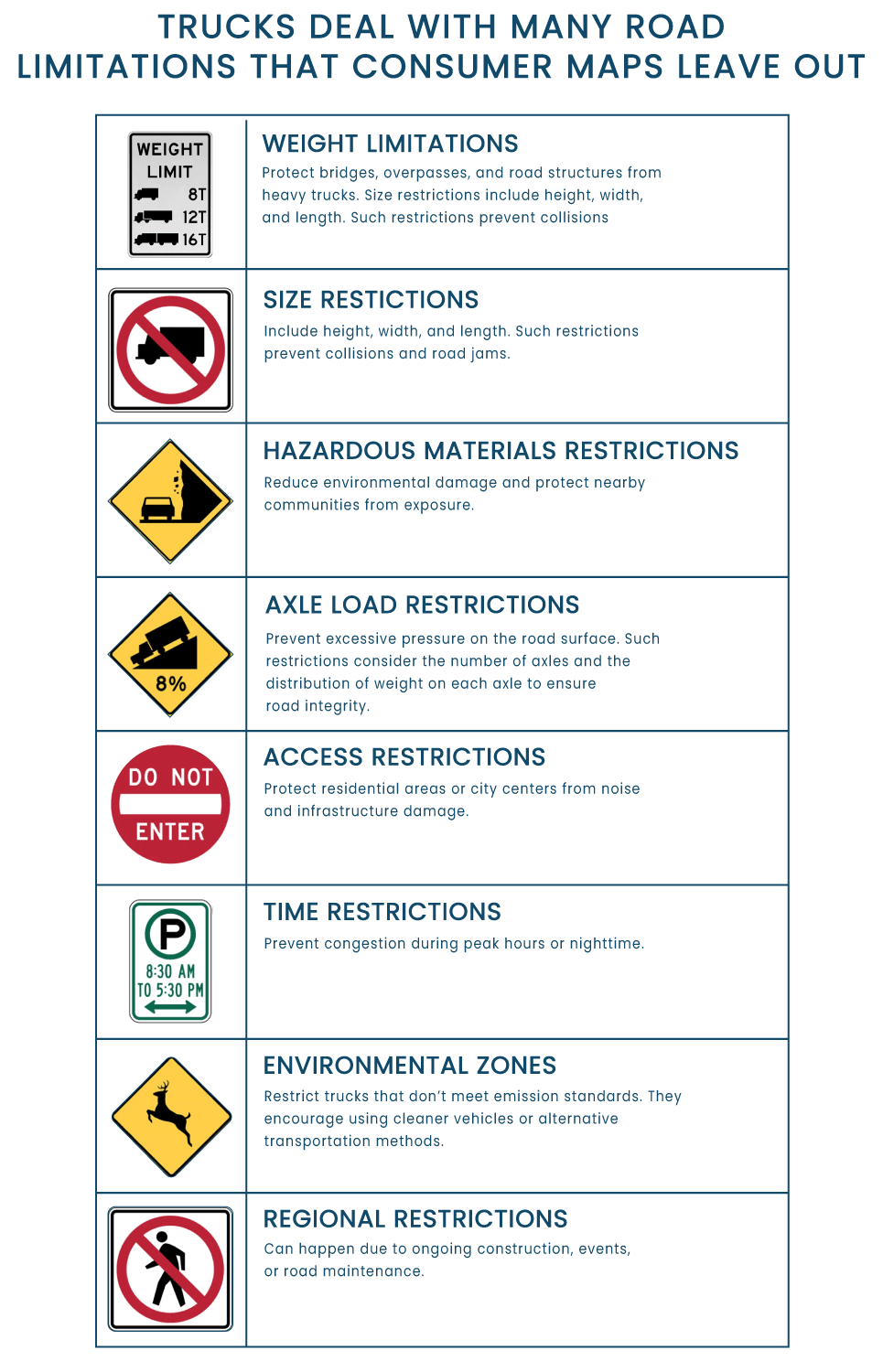
For example, trucks deal with many road limitations that consumer maps leave out:
- Weight Limitations protect bridges, overpasses, and road structures from heavy trucks.
- Size Restrictions include height, width, and length. Such restrictions prevent collisions and road jams.
- Hazardous Materials Restrictions reduce environmental damage and protect nearby communities from exposure.
- Axle Load Restrictions prevent excessive pressure on the road surface. Such restrictions consider the number of axles and the distribution of weight on each axle to ensure road integrity.
- Access Restrictions protect residential areas or city centers from noise and infrastructure damage.
- Time Restrictions prevent congestion during peak hours or nighttime.
- Environmental Zones restrict trucks that don’t meet emission standards. They encourage using cleaner vehicles or alternative transportation methods.
- Regional Restrictions can happen due to ongoing construction, events, or road maintenance.
If you choose Google Maps, Mapbox, or OpenStreetMap for your application, you’ll need to create custom map layers with the road restrictions.
Both MapBox and Google Maps are great at customization. With both, you can create custom layers on top of the maps. The difference is that in Google Maps you have to use the default base layer, while in Mapbox it’s optional.
TomTom has inbuilt vehicle restrictions in Northern America and Europe. At the same time, the API is not very customizable, so you can’t add vehicle restrictions for the rest of the world.
Custom styles
You can create custom styles for all 4 maps. Alternatively, you’re free to choose a premade style. This would save you time on custom design.
Google Maps has thousands of styles by Snazzy Maps. Other map providers have fewer options.
Offline maps
This must be the only case where Google Maps is defeated. The Platform specifically prohibits caching, so you can’t use the maps offline:
(b) No Caching. Customer will not cache Google Maps Content except as expressly permitted under the Maps Service Specific Terms.
All the other maps are just fine offline.
Street view
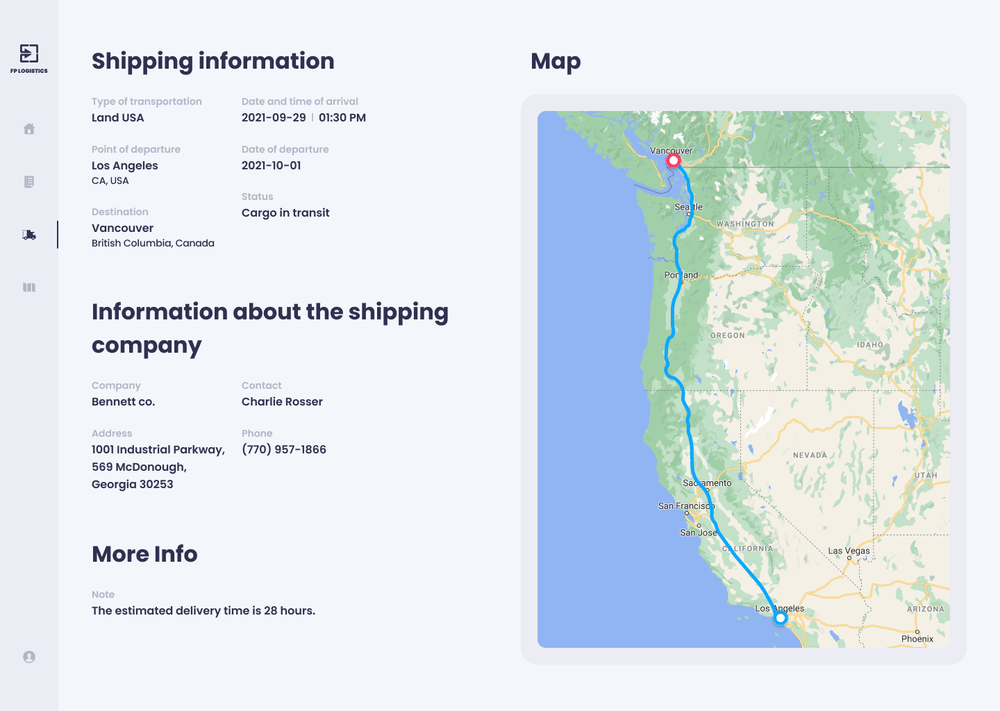
Street view can come in handy for delivery drivers. When you don’t know your way around the city, you can have trouble finding the specific building and entrance. Street View can provide precise delivery instructions to drivers, so they don’t have to think twice about the location.
Google Maps has the most robust street view out there. The other companies that we’re comparing today don’t provide street view at all. But you can import 3rd party street view layers into Mapbox or OpenStreetMap.
When to Use Each Map?
Choose Google Maps for logistics software when you need worldwide traffic data and strong customization options, and seamless integration with other Google services.
Use TomTom for logistics software when you need robust ready-made layers, reliable coverage, and efficient routing algorithms. It is particularly useful for fleet management and asset tracking applications.
Consider OpenStreetMaps when you require a free solution with customizable maps, open data, and the ability to contribute to the map’s accuracy. It is suitable for developers looking for flexible integration options and who prioritize community-driven map data.
Get Mapbox when you need highly customizable and cheap maps. You’ll get the ability to add custom layers, and fine-grained control over visual appearance and functionality. It is suitable for developers looking to build custom mapping solutions and prioritize flexibility in integration options.
Here’s How to Find the Right Map Platform:
- Think About Your Requirements. Do you need specific features like street view or offline mode?
- Consider Your Region. In Asia, Southern America or Africa you’ll have a hard time tracking traffic in real time. That is, unless you use Google Maps or local services.
- Calculate About Your Budget. Google Maps is an expensive solution. Not only will you pay for the Platform, but you may also need to spend extra on custom layers.
If you need help choosing the right map, get in touch for a free consultation. At Aristek, we’ve been building logistics software for 10 years. We’ll find the right map for your project and budget.