In the early days of web development, all sites had a collection of HTML and CSS files and were static. Then PHP and SQL joined this technology stack with a huge army of CMS systems. The rapid growth in popularity of WordPress, Drupal, MODx, and other CMS web development has entered a new era — MPA or Multi Page Applications. MPAs are multi-page applications that work like the websites we are used to. MPAs send a request to the server and completely update the page when any action is performed on it (going to another page, entering and changing data).
This approach allows you to manage content on the fly and provides developers with a fairly flexible learning curve and deployment of web applications. The MPA development approach was considered ideal. Until it became clear that such web applications do not meet the increasing requirements for security, traffic stability, download speed, SEO optimization, and protection from DDOS attacks. Development and support of custom MPA applications have become labor-intensive and resource-intensive, and as a result, expensive for the client.
Not so long ago, the classic approach to building websites has a worthy competitor — Jamstack, which combines all of its MPA advantages and solves its shortcomings, but first things first.
What is Jamstack?
The term Jamstack was coined by Matthias Bielmann, co-founder of Netlify. Jamstack is not a technology, but rather a non-traditional web development approach.
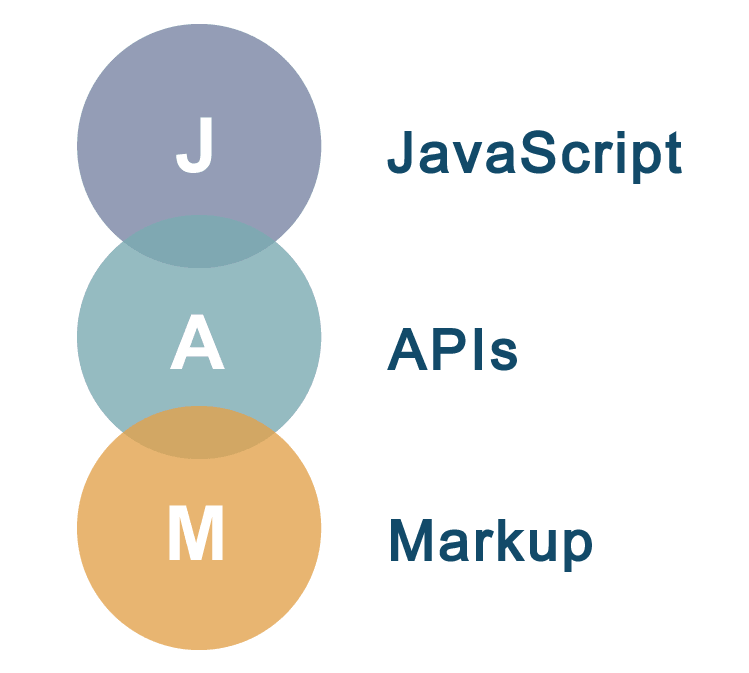
Within the Jamstack approach, developers understand the web technology stack, which consists of:
- “J” (JavaScript) is a programming language for rendering on the user side. Front-end frameworks are used, for example, Vue.js, React, Angular, or even basic JavaScript.
- “A” (API) – application programming interface that allows you to integrate additional functions on the server side;
- “M” (Markup) – the basis of the site, its main frame. It is formed during assembly. Usually, for content sites, this is done using a site generator. (for example, GatsbyJS, Nuxt.js, etc.)
You can better understand how Jamstack works by looking at how it differs from MPA. The graph is very simplified, but clearly shows what is happening under the hood.
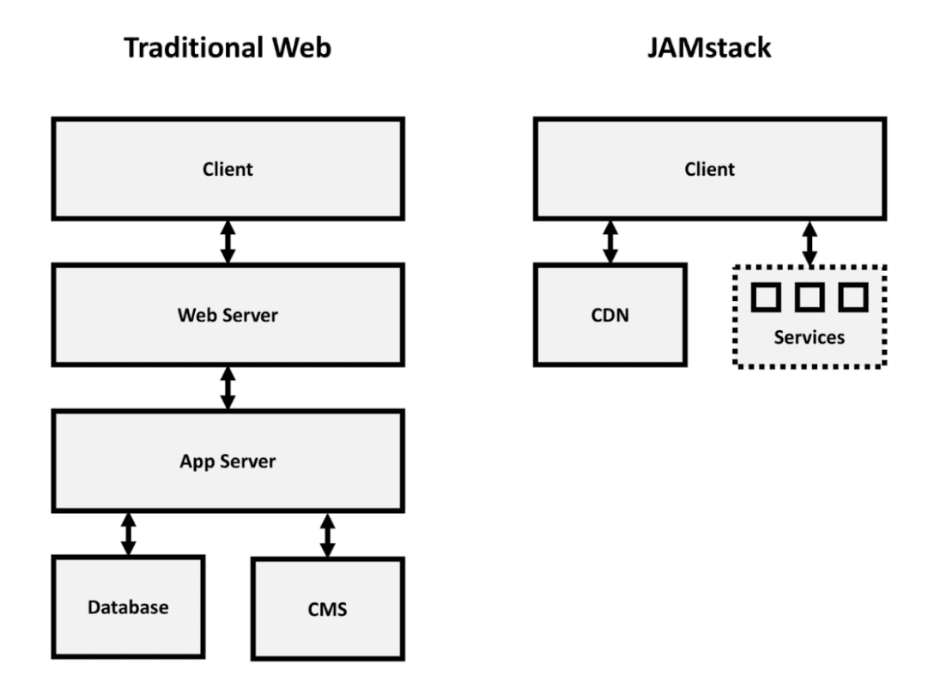
Differences between traditional server websites & Jamstack sites
Now let’s clarify the differences a little more.
Traditional Server Sites:
- When the user contacts the server, the hosting starts processing the request, executes a series of chains of queries to the database and the server, then generates an HTML page and gives it to the user;
- Codebase update is done via FTP/SFTP connection;
- The database is a separate entity that requires maintenance.
- CMS is used for content management.
Jamstack evolution
At the very beginning of its existence, Jamstack was suitable for the implementation of small commercial sites and blogs. Then comes the rapidly growing community and the development of its approach. It also increased the functionality of static web applications significantly. At the moment, Jamstack integrates with a large number of microservices that allows you to implement large-scale products from commercial sites to e-commerce.
Market giants such as Peloton, Louis Vuitton, Bang & Olufsen, LEGO, Bitcoin, and many others have chosen Jamstack for their network products. The growth in popularity of Jamstack can be seen here:
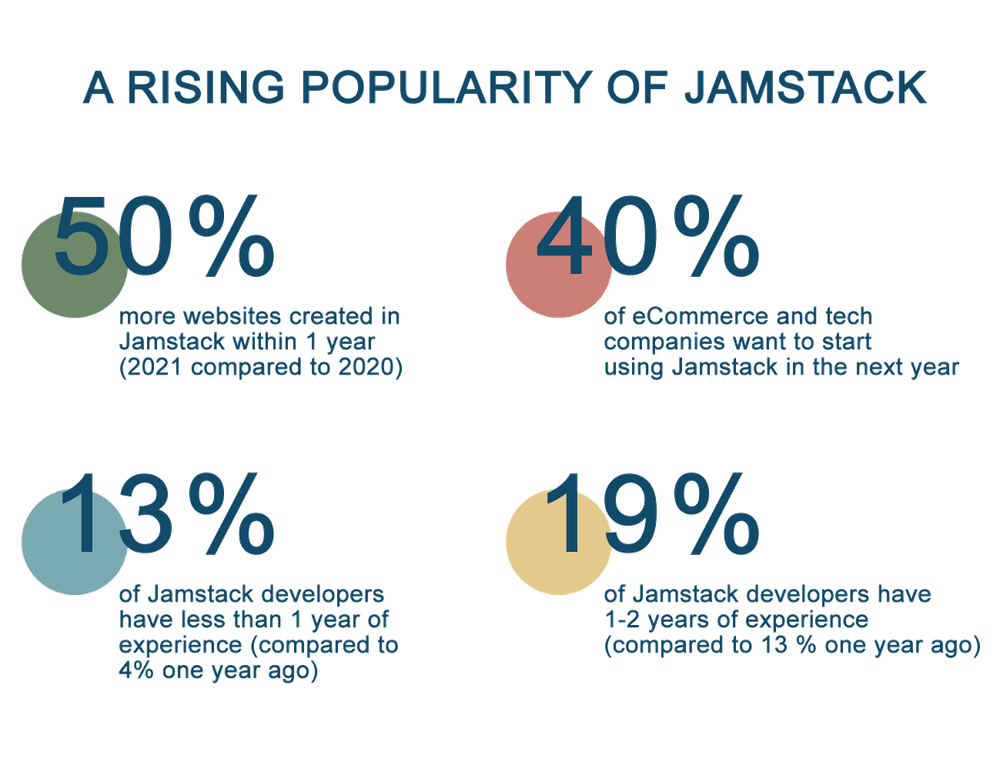
Why Jamstack?
Who is Jamstack for?
Jamstack will be the best choice if you are creating or updating your internet project and your project does not contain complex dynamic logic. Jamstack will allow you to get fast, productive and scalable solutions in a short time.




