Here be dragons. In ancient maps, that phrase signaled uncharted territory. Fast forward to today, and it feels like we’re standing on the edge of similar uncharted waters with artificial intelligence. It’s everywhere now, from your Netflix recommendations to the face recognition software in your phone.
But how many of us really know what’s happening behind the scenes of artificial intelligence as we know it?
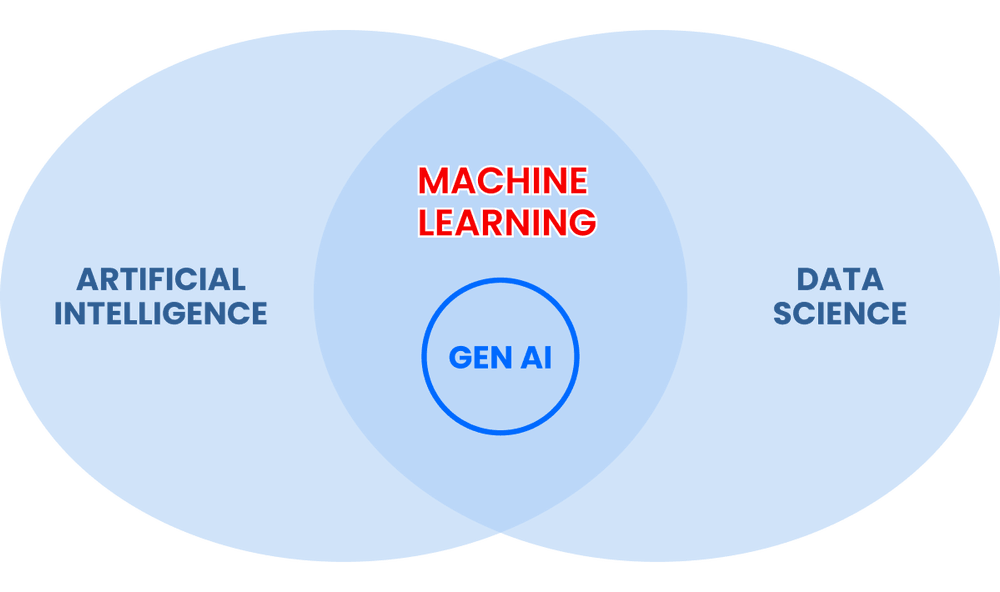
Behind what may seem like simple, intuitive tools lies a complex ecosystem of data analysis, sophisticated algorithms, and powerful computing infrastructure. To understand all this, we need to introduce other essential terms like machine learning, data science, and generative AI. Let’s break them down to better understand how they work together.
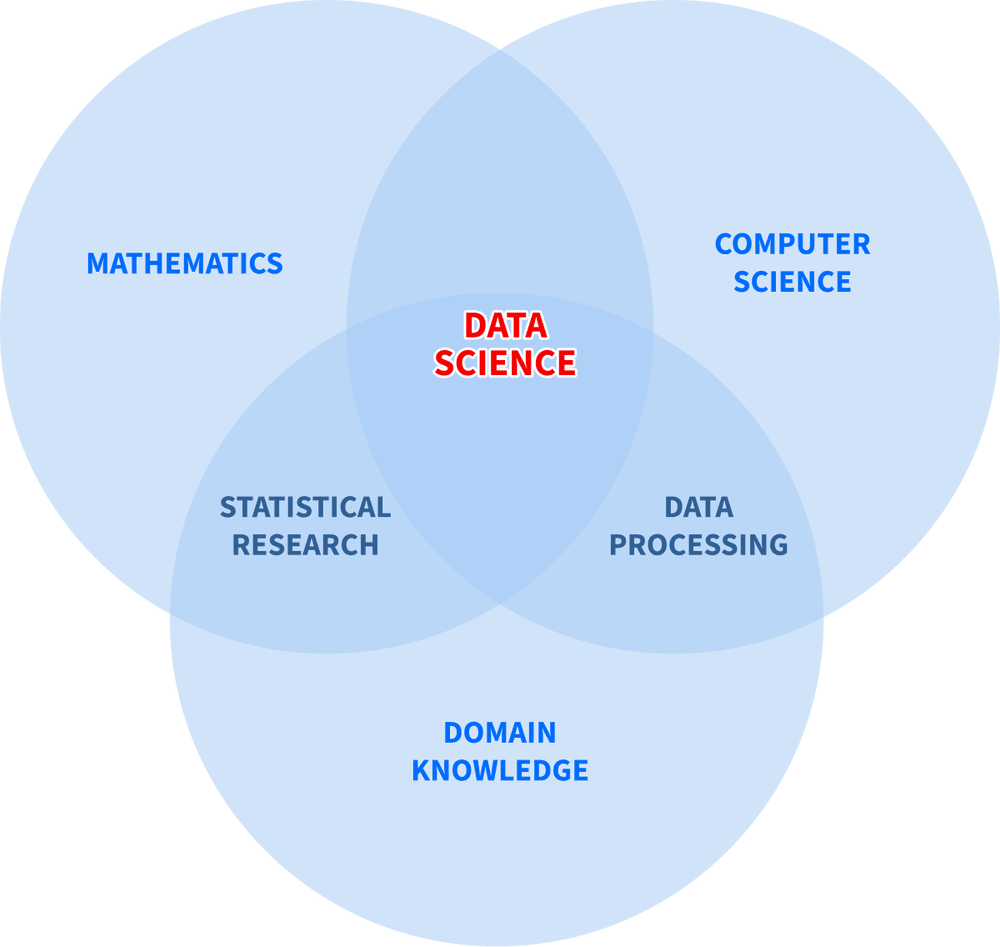
Data science
Everything in AI begins with data. Data science is a vast, diverse field that finds value in huge data sets. It uses advanced tools to examine raw data, collect it, process it, and derive insights that provide meaning.
However, it’s important to remember that data science is more than just a cog in the AI machine; it’s a standalone discipline. While AI often relies on data science for input, data science has its own goals and methods, independent of AI.
Data scientists use techniques like statistical analysis, machine learning models, and data visualization to uncover patterns in data. These insights can be applied across many industries — healthcare, finance, retail, and more — without necessarily involving AI. Data science focuses on understanding data and drawing actionable conclusions, while AI takes it a step further by using these insights to simulate human intelligence or automate processes.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, is a machine’s ability to carry out mental operations often associated with human minds. While AI and data science intersect in many areas, AI is more focused on replicating human cognitive functions — such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making — whereas data science is primarily concerned with understanding and interpreting data.
For instance, when AI is used to uncover insights or patterns in data (like predictive analytics), it falls under the domain of data science. AI technologies like speech recognition, computer vision, and generative models work to process information and make decisions, without always needing the deep data analysis that data science provides.
There are two categories of AI:
- General AI possesses generalized human cognitive abilities. It can understand, learn, and apply intelligence to a wide range of tasks, much like a human can.
- Narrow AI performs a specific task or a limited set of tasks. It operates within a predefined scope and doesn’t possess general intelligence or understanding outside its designated domain.
How AI works
AI systems rely on several core technologies, though the specifics vary. At its core, AI converts different data types — such as text, images, and videos — into numerical formats and identifies patterns and relationships among them. This process requires training; similar to how humans learn from existing knowledge, AI systems are fed large datasets to “learn” from.
Some of the key technologies behind AI include:
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Computer vision
- Speech recognition
- Generative AI.
Do you have concerns about AI implementation?
Need an analysis of your data or existing AI solutions? Are you looking to develop a custom AI solution or integrate existing AI apps into your system?
Aristek can assist with any request regarding AI consulting and development
Machine learning
Machine learning is a subset of both AI and data science. This is a type of AI capable of adapting to various inputs, such as extensive historical datasets, generated data, or user-provided information.
Some ML algorithms can train themselves to identify patterns in data; this process is called deep learning.
When businesses implement AI software, they are probably deploying ML. This technology is behind most predictive texts and chatbots, language translation applications, the movies Netflix recommends, and the content you see on your social media feeds.
How machine learning works
Machine learning is both simple and complex. It uses algorithms (sets of rules) that are refined over time by learning from past data. For example, an algorithm can be trained on thousands of labeled flower images to later identify flowers in new photos based on what it learned.
Training can be supervised, where the algorithm learns from labeled data, or unsupervised, where it finds patterns in data without labels. Once trained, these algorithms become machine learning models that can predict, sort, or recognize data.
It’s a bit like teaching a child to recognize numbers by showing them images and telling them the names. Over time, the child learns to identify them correctly.
Generative AI
Generative AI lies between data science, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. To be more precise, GenAI is a complex deep learning model that can generate high-quality content based on the data it was trained on.
GenAI deals with different types of data and generates different types of content, including images, audio, code, simulations, and videos..
The turning point of generative AI development was the release of ChatGPT in 2022. The technology showcased the impressive abilities to understand and generate human-like text and gained significant attention for its capacity to hold coherent conversations, answer questions, and assist with tasks like creative writing and coding.
How generative AI works
Generative AI learns from huge amounts of data, training on everything from text to images so it can understand and respond to prompts in everyday language. Unlike older models that are built for one specific job, generative AI can handle a wide range of tasks.
It’s like a creative black box: you give it an input — text, an image, or even a sound — and it generates something entirely new based on what it’s learned. But you shouldn’t always rely on its output. Sometimes, generative AI can be like that overconfident friend who “knows everything” — and then tells you Paris is the capital of Italy.
The outputs it creates can sound incredibly convincing. This is by design, but occasionally, the information it generates can be wrong or even biased.

That said, the technology is still in its early days. As research moves forward, there’s a strong chance that this tech will drastically change how we create content, and a smart but prone to the occasional mess toddler will turn into the wise and all-knowing Yoda.
Let’s sum up
AI is an umbrella term for technologies that enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. It encompasses data science, which analyzes large datasets for insights; machine learning, a subset that learns from data to improve performance; and generative AI, which creates new content based on what it has learned.
Want to learn more about AI, its solutions, benefits, use cases, and other essential insights? Explore our guide to AI. We also encourage you to check out our blog for more technical news and insights.
If you’re ready to adopt AI or have concerns about the process, book a free consultation with our experts!
Discover how we transformed learning for an eLearning provider with an AI-driven question-answering system.
Our chatbot fills the gaps when teachers can’t help – answers questions in seconds, handles over 1,000 inquiries per minute, and provides 24/7 personalized support.
Need expert solutions or want to explore new AI opportunities? We’re here to help!