What’s the real cost of a task no one complains about?
Manual report updates, email filtering, form validation – these jobs rarely make it to priority lists. But done hundreds of times a day, they quietly take over hours, sometimes entire roles.
Most companies don’t notice these tasks until they start looking closely. Then it becomes clear: the issue isn’t big decisions, it’s small routines that pile up.
In this article, we look at how AI process automation works in practice, which business areas benefit most, and what a realistic path to adoption looks like.
What AI automation means
Artificial intelligence automation is what happens when software doesn’t just follow rules; it learns patterns, adapts to context, and makes decisions based on data.
Unlike traditional automation, which depends on clear step-by-step instructions, AI automation works where instructions don’t quite fit. It uses models trained on real examples to handle input that’s unstructured, incomplete, or unpredictable. That includes free-form emails, scanned documents, support tickets, logs, audio, or messy spreadsheets.
Behind the scenes, it combines a set of familiar technologies.
- Machine learning helps systems recognize patterns and make predictions, for example, detecting duplicate invoices or sorting support tickets by urgency.
- Natural language processing makes sense of human text, extracting order numbers from emails or pulling intent from customer queries.
- Predictive analytics adds context, using past behavior or trends to inform what should happen next.
In practice, this means that AI automation isn’t just about doing things faster. It’s about letting systems decide what to do next when the path isn’t explicitly mapped out.
But AI is just one piece of the puzzle.
What many companies are actually building is intelligent automation, where artificial intelligence, robotic process automation (RPA), and business process management (BPM) work as one system.
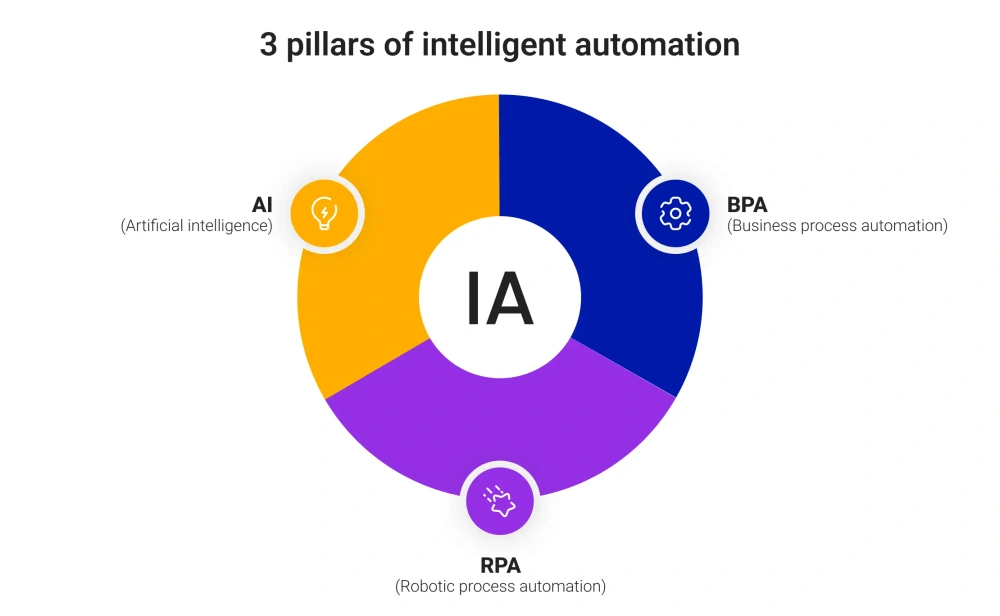
AI handles judgment, RPA handles execution, and BPM handles the logic that connects everything across systems. In this setup, automation is no longer limited to repeatable tasks. It can follow complex workflows, switch context, and adapt when inputs don’t match the template.
So, the value doesn’t come from AI alone, but from how it fits into a larger structure – one where manual steps gradually get replaced by a system that knows when to act, what to check, and when to ask for help.
How fast is AI moving? Faster than you think
AI automation is already being built into the daily operations of businesses across industries as part of how processes are structured and scaled. But how widespread is it? And who’s actually using it?
Let’s look at what the numbers show about where AI stands today and how its role in automation continues to grow.
According to Eurostat data, European enterprises are steadily adopting AI technologies. The latest numbers show a clear upward trend from 2023 to 2024.
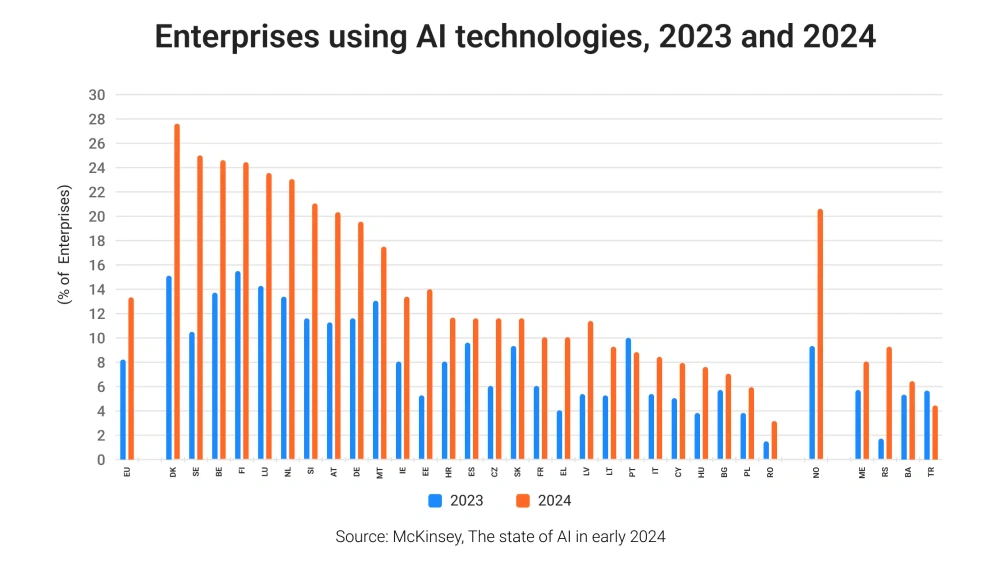
While large companies continue to lead in adoption, the shift is not limited to them. The number of small and medium businesses using AI is also rising:
- In 2023, 6.38% of small and 13.04% of medium enterprises in Europe reported using AI.
- In 2024, that number grew to 11.21% of small and 20.97% of medium enterprises.
We don’t yet have data for 2025 to confirm the next step in this curve, but several trends suggest that adoption is only accelerating:
- First, there’s a visible shift in business intent: more companies are not just experimenting with AI but allocating budgets to embed it in operations.
- Second, the entry barrier is dropping. Tools are more accessible, and AI capabilities are becoming easier to integrate, even without deep in-house expertise.
- Third, the competitive pressure is rising. As automation proves its value in reducing delays and increasing process stability, doing nothing becomes a bigger risk.
Supporting this direction, 92% of companies say they plan to increase their AI investments over the next three years, according to McKinsey’s 2025 report. This signals a structural change in how businesses plan for the future.
Another study from Accenture backs this up: 69% of executives say the rise of AI brings a new urgency to rethinking how technology systems and business processes are designed, built, and run.
Don't chase trends. Build AI that solves real problems.
Explore our AI development & integration services.
What processes are actually being automated today
AI can support everything from factory planning to legal reviews, but we’ll stay focused on the core business processes most companies share.
Customer service
Customer service teams deal with high volumes of repetitive queries, complex customer expectations, and pressure to respond quickly across multiple channels. When wait times increase or answers sound generic, customer satisfaction drops, and so does brand trust.
This is where AI can help. Generative AI and other technologies help teams respond faster, resolve issues automatically, and even prevent problems before they arise.
A 2024 Salesforce survey found that 63% of service professionals believe generative AI will speed up their work.
Gartner projects that by 2025, 80% of support organizations will apply generative AI in some form to improve both agent productivity and customer experience.
So how does AI make that possible?
- Chatbots can resolve common questions instantly, 24/7, without waiting in a queue.
- Predictive analytics identify customers likely to churn or escalate, helping agents intervene early.
- Sentiment analysis detects tone in real time and flags frustrated users, allowing for smarter triage.
- Generative AI can draft responses, summarize previous interactions, and offer on-brand language suggestions to support agents.
Real-world examples are everywhere. American Express applies AI to route customer requests to the most suitable support channel, reducing resolution time and improving satisfaction scores.
Meanwhile, Airbnb uses machine learning to detect tone in user complaints and automatically adjust escalation logic based on urgency.
Marketing & sales
Among all functions, marketing is the most active field for AI adoption, according to McKinsey. And that’s not surprising. Marketing sits on large volumes of customer data, works on short cycles, and demands personalized, scalable content – a perfect match for AI.
Generative AI, in particular, is changing how marketing teams approach:
- Customer experience, by enabling real-time personalization across websites, emails, and ads
- Audience segmentation, with algorithms identifying high-conversion clusters based on behavior, location, or preferences
- Campaign performance, with AI generating A/B test variants and optimizing content on the fly
- Creative content production, including visual assets, captions, and even product copy
These improvements also affect sales. AI tools help sales teams forecast deal probability, suggest next steps, and prioritize leads not based on intuition, but based on behavior patterns and past performance.
According to McKinsey, around 20% of current sales activities could be automated using existing AI tools. These include drafting outreach emails, updating CRM records, and even guiding conversations through AI-generated talking points.
Major companies are already acting. HubSpot offers its clients built-in AI tools that write outreach emails and suggest engagement strategies based on lead behavior. Netflix uses AI to analyze behavior and recommend personalized help content based on what users are watching and searching.
Read the article to learn how AI takes content personalization to the next level.
Discover how we created an AI-based behavior analysis & sales forecast solution for a giant retailer.
Invoice processing
Invoice processing is one of the most established areas where AI adds measurable value. Traditionally, it involves time-consuming tasks: extracting data, verifying details, matching purchase orders, and entering values into ERP systems.
AI simplifies and speeds up each step.
- Data extraction: Machine learning models identify and pull relevant information from invoices, even when layouts vary.
- PO matching: AI cross-references invoice data with purchase orders and receipts automatically.
- Fraud detection: AI spots duplicate payments or irregular amounts based on historical data.
- Exception handling: It flags inconsistencies for human review, rather than blocking the entire process.
For finance teams, this means fewer delays, fewer errors, and less manual input. It’s also a foundation for broader automation of accounts payable processes.
Finance & accounting
Nearly 70% of financial services firms reported revenue increases attributed to AI, according to 2024 Statista data. Most of these organizations saw gains in the 5–10% range, driven by improvements in forecasting, customer service, and cost reduction.
AI plays a central role in modern finance by addressing long-standing challenges:
- Fraud detection: Algorithms monitor transactions in real time, identifying unusual activity and
reducing exposure to financial crime. - Forecasting and scenario modeling: AI helps CFOs model best- and worst-case outcomes, improving agility in budgeting and planning.
- Automated reconciliation: AI matches payments, bank statements, and invoices, minimizing manual intervention.
- Regulatory compliance: Natural language processing helps monitor changes in regulations and automate compliance reporting.
Generative AI is also finding its place in accounting workflows. It is actively being used for tasks, like generating reports and summarizing financial statements, helping teams accelerate close cycles and reduce reporting bottlenecks.
Goldman Sachs uses AI to analyze market data and support its trading decisions. JPMorgan Chase uses AI to review legal documents and identify contractual risks – tasks that would take humans much longer.
Learning & development
Learning and development is one of the fastest-growing fields for AI application, especially in eLearning. As more companies shift to remote and hybrid models, the way learning is delivered is also evolving. AI is central to that evolution.
In this context, AI plays several roles:
- Adaptive learning paths personalize the training flow based on a learner’s performance and knowledge gaps.
- AI-powered content creation tools generate training materials, questions, and scenarios with less manual input.
- Interactive modules built with AI adjust in real time to user responses, making learning more engaging and relevant.
- Automated feedback systems assess open-ended answers, provide instant corrections, and help learners improve without instructor intervention.
- Continuous optimization ensures that training materials evolve based on learner feedback and analytics, not static design.
This approach is already delivering results. According to recent 2024 research, AI-powered training increases knowledge retention by 25%, and McKinsey estimates $60 billion in potential savings from automating educational content creation alone.
Сybersecurity
Cybersecurity is one of the areas where AI has found its place quickly – and for good reason. With organizations depending on interconnected systems, cloud services, and digital platforms, the risk surface grows daily. So do the tools used by attackers.
Traditional defense methods struggle to keep up with threats that are automated, adaptive, and often invisible until it’s too late.
That’s where AI proves useful:
- Real-time threat detection: AI models monitor networks continuously, flagging unusual behavior before damage is done.
- Security reporting: By automating data collection and report generation, AI reduces the time spent on routine analysis.
- Vulnerability scanning: AI reviews code, systems, and user activity to find potential weak points before attackers do.
- Threat intelligence: It connects the dots between different attack patterns and builds early warning systems for future incidents.
- Automated incident response: AI can isolate compromised systems, block malicious IPs, or deploy patches without human intervention, cutting response time from hours to seconds.
Below are some of the key benefits of integrating AI into cybersecurity systems:
Can AI guarantee 100% protection? No system is completely attack-proof. But AI improves visibility, response time, and accuracy, turning cybersecurity into a more proactive and resilient process.
To see how companies already use AI in cybersecurity, read the full article.
Supply chain operations
AI strengthens supply chains by turning them from reactive to predictive. Instead of responding to disruptions after they occur, AI helps anticipate them and act earlier.
Here’s how AI supports supply chain operations:
- Demand forecasting: Machine learning models predict sales based on historical data, seasonality, weather, and economic indicators.
- Dynamic pricing: AI adjusts prices in real time based on inventory levels, competitor pricing, or local demand fluctuations.
- Route optimization: AI identifies the most efficient delivery routes based on traffic, fuel costs, and shipment urgency.
- Risk detection: AI monitors supplier behavior and external signals to detect early warning signs of delays, disruptions, or quality issues.
- Automated inventory replenishment: AI analyzes sales velocity, lead times, and warehouse data to trigger purchase orders autonomously, minimizing stockouts and excess inventory.
Some companies use AI to manage warehouse robotics and automate stock replenishment based on demand projections. Others, like Zara and many others, rely on AI to align production with in-store data, keeping inventories lean and reducing markdowns.
McKinsey reports that AI-enabled automation can drive:
- 20–30% reductions in inventory
- 5–20% lower logistics costs
- 5–15% savings in procurement spend
Research & development
McKinsey estimates that AI could accelerate R&D by 20% to 80%, depending on the industry. For businesses, it means earlier market entry, fewer failed experiments, and smarter allocation of research budgets.
AI supports the R&D process in several ways:
- Data mining and pattern detection: AI can scan thousands of research papers, patents, or test results to surface trends and hidden correlations.
- Simulations and digital twins: In engineering and manufacturing, AI models simulate designs in silico before building physical prototypes, reducing trial cycles.
- Hypothesis generation: Generative AI can suggest novel compound structures or product features based on success patterns from prior research.
- Optimization: Algorithms test multiple configurations to find the best-performing combination of variables – in drug formulation, material science, or software design.
Pharmaceutical leaders like Novartis use AI to accelerate early-stage drug discovery, cutting years off traditional lab timelines. Now, scientists make breakthroughs in weeks, even days.
Business planning
Modern business planning is no longer an annual ritual; it’s a constant, high-stakes balancing act. Companies must contend with inflation, labor shortages, supply chain volatility, and shifting customer demand. These pressures strain traditional planning methods, which are often slow, manual, and siloed across departments.
AI introduces a new level: autonomous planning. It’s a data-driven approach supported by AI, where systems monitor input signals, like inventory levels, demand shifts, or pricing changes, and adjust plans in real time without waiting for human intervention.
Autonomous planning is enabled by a combination of technologies:
- Machine learning models for demand forecasting and inventory optimization
- Predictive analytics to anticipate supply constraints or customer behavior
- AI-powered scenario planning tools that test responses to possible disruptions
- Natural language generation to automatically build reports and recommend decisions
Retailers like Walmart and Target use AI-driven demand planning to fine-tune inventory levels in response to regional sales patterns, events, or economic indicators.
As a result, they have more resilient operations, faster response to disruptions, and a tighter alignment between strategy and execution.
Bottom line
What we’ve just covered are only the most common applications of AI. In practice, its reach goes far beyond these.
Legal operations, procurement, internal communications, document classification, predictive maintenance – these are other processes where AI tools already prove useful.
AI doesn’t belong to one department. It finds application wherever there’s repetitive work, large amounts of data, or decisions that benefit from faster, smarter insight.
But that doesn’t mean everything needs to be automated. Businesses should focus on the processes that really drain time, are prone to errors, or hold back growth.