According to a recent McKinsey survey, 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function – a steady climb from 72% earlier in 2024 and just 55% a year before.
AI adoption grows fastest in places where the tasks are repeatable and mistakes are expensive. Document review, inspection, forecasting, routing, matching, classification and many others fall into this category. Companies rely on models for these tasks because they scale well and deliver stable output.
If you’re interested in automation but unsure where to start, we’ve put together a collection of real use cases across multiple industries. Not theories, not future ideas, but real examples that run in production today.
Read, explore, and see what might fit your next project.
AI use cases in education and corporate training
1. Automated grading & feedback for assignments
Models review written answers, short essays, code submissions, or quizzes and score them based on rubrics. They also produce short feedback pointing to mistakes or gaps in understanding.
This cuts teachers’ workload, speeds up feedback cycles, and helps LMS platforms scale without raising instructor hours.
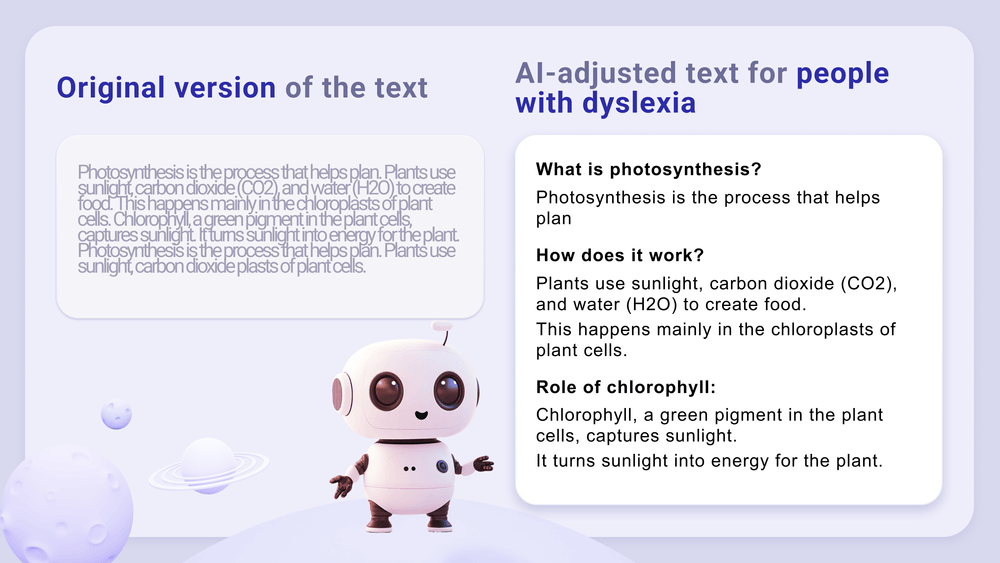
2. Content adaptation for accessibility
Systems track how a learner performs across modules and adjust the path by offering simpler explanations, harder tasks, or missing modules and adapting to the learner’s unique needs, for example, dyslexia.
The system improves completion rates, reduces dropout levels, and gives students a more effective learning experience.
3. Сontent generation for learning materials
Models assist instructors by creating summaries, explanations, real-world examples, lesson scripts, and variations of exercises. They can also convert existing content into different formats.
Thanks to this, educators produce fresh materials faster which reduces the cost of building new courses.
4. Round-the-clock student support
Students ask questions in natural language. An AI question-answering system uses course content, textbooks, and lecture materials to form accurate answers.
This reduces dependency on instructor availability and supports continuous learning outside class time.
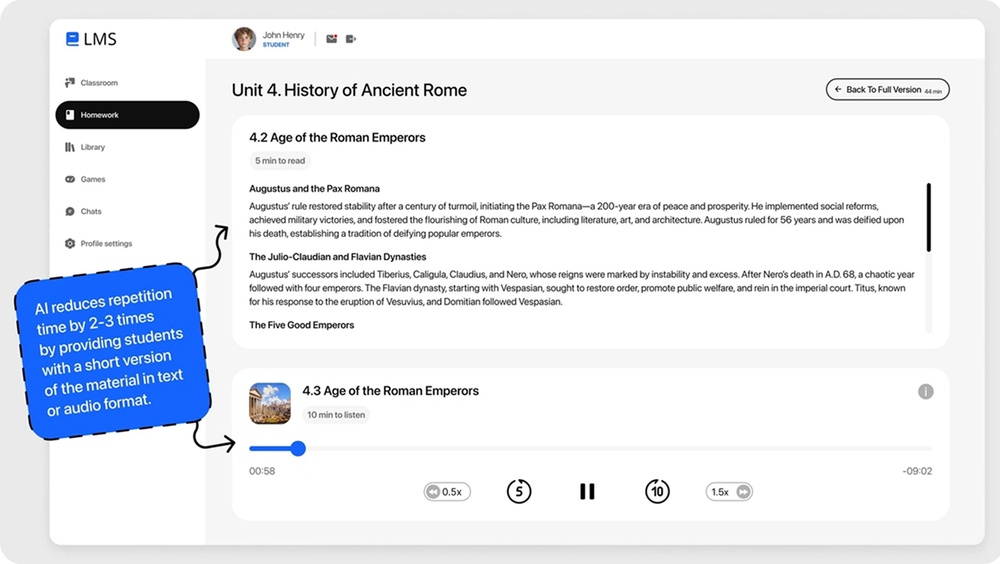
5. Speech-to-text & text-to-speech for accessibility
Speech recognition converts lectures into transcripts. Text-to-speech tools read course materials for people with visual or learning difficulties taking into account accents, intonation, specific vocabulary, and other things.
This supports better accessibility, improves engagement for diverse learners, and helps institutions meet compliance requirements.
6. Highlight generation from video lectures
AI models scan lecture recordings and mark key moments, important explanations, timestamps with examples, and short summaries.
Learners save time, review faster, and navigate long videos without losing critical points.
7. Personalized coaching
AI coaching systems simulate real conversations, negotiations, interviews, or professional scenarios. They react to the learner’s input and give guidance or corrections and create learning roadmaps.
This helps people practice soft skills, prepare for real-life situations, and build confidence without needing a live instructor.
8. Skills gap analysis & curriculum mapping
Models analyze learner performance and compare it to job requirements or certification standards. They show where skills are missing and recommend courses to close the gap.
Thanks to this tool, institutions align programs with job market needs and help organizations train their workforce more effectively.
9. Data analytics for performance improvement
This is a data management solution that collects and analyzes platform usage and engagement metrics to know district and school performance and other key factors affecting learning experience.
By tracking student progress and pinpointing gaps in learning content, you can boost curriculum effectiveness.
10. Automated proctoring & academic integrity monitoring
Computer vision tools detect suspicious movements, additional devices, or outside help during online exams. They also check audio cues and browser activity.
As a result, cheating is reduced, certification value is protected, and institutions can run remote exams at a larger scale.
Retail & eCommerce
11. Personalized product recommendations
AI models analyze browsing behavior, past purchases, time spent on product pages, and similar customer actions. Based on these patterns, they generate suggestions that match a shopper’s interests. This works on product pages, in search results, and in cart reminders.
For a retailer, this increases the number of items viewed per session and often raises the average order value because customers see items that match their intent rather than generic picks.
12. Demand forecasting
Forecasting models combine historical sales, promotions, weather data, shelf life, local events, and other signals to estimate demand for each SKU. They react to changes faster than manual planning.
Accurate forecasts reduce waste for perishable goods, help plan warehouse capacity, and support smarter purchasing decisions.
13. Visual and voice search
Visual search allows customers to upload an image and get items that look similar. Computer vision models detect color, shape, texture, and product attributes and return the closest matches in the catalog.
Voice search uses speech recognition and natural-language models to interpret spoken queries, even when phrased informally.
Both features reduce search friction and help users find products faster, especially when they cannot describe the item clearly.
14. Dynamic pricing and discounts
Pricing models process historical sales, seasonality, competitor prices, stock levels, and demand signals. Based on these inputs, AI proposes updated prices or discount levels that keep items moving without eroding margins.
Retailers use this to avoid stockouts or overstocks, react to market shifts within minutes, and maintain more stable revenue per product category.
15. Chatbots and virtual shopping assistants
Chatbots can answer questions about delivery terms, product details, returns, or availability. They handle large volumes of requests by matching user messages to predefined intents or generating responses using controlled language models.
This removes many simple tasks from human agents and gives customers quick answers during peak hours, which reduces abandonment and support waiting time.
16. Inventory and supply chain optimization
AI systems track demand signals, supplier lead times, transit delays, and restock patterns. Forecasting and optimization models use this data to propose reorder points, adjust safety stock, and plan distribution across warehouses.
Retailers rely on this to reduce shortages, avoid long-term stockholding costs, and keep products available in regions where they are moving fastest.
17. Customer support
AI tools classify incoming messages, route them to the right team, suggest replies to agents, or answer the simplest questions automatically. These customer support tools can also summarize long complaints or extract key fields from customer emails.
This shortens resolution time and allows support teams to focus on cases that require human decisions.
18. Visual discovery and “style matching”
Computer vision models compare products based on shape, color palette, patterns, and design details. When a user clicks on an item, the system can present visually similar alternatives or complete-the-look suggestions.
This increases the number of items explored and helps customers move from inspiration to purchase when the exact product is unavailable.
19. Personalized marketing and email campaigns
AI segments customers by behavior, recent actions, spending patterns, and browsing history. It then selects the right timing, channel, and content for emails, ads, or push notifications.
This reduces irrelevant messages and increases conversions because each campaign reflects what the customer is actually researching or planning to buy.
Healthcare, pharmaceutical, and veterinary
Now, let’s look at how AI is adopted in healthcare.
20. Medical imaging analysis & diagnostics
Computer vision models review X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasound images. They detect patterns linked to tumors, fractures, infections, or organ abnormalities with consistent accuracy. The system highlights suspicious regions or provides probability scores for specific conditions.
This reduces diagnostic delays, supports radiologists during peak workload, and helps hospitals handle higher imaging volumes without lowering quality.
21. Accelerated drug discovery & repurposing
AI models screen large molecular libraries, predict molecular interactions, and estimate toxicity or efficacy before lab testing. They also match existing drugs to new disease targets by comparing biological pathways.
This shortens early research cycles, reduces the number of failed experiments, and helps pharmaceutical companies move promising candidates to testing faster.
22. Predictive analytics for patient deterioration
Models analyze patient vitals, lab results, medication history, and clinical notes. They detect early signs of deterioration such as sepsis, respiratory decline, or cardiac events.
This supports faster intervention, reduces ICU admissions, and helps care teams allocate resources efficiently.
23. Personalized medicine and treatment planning
AI systems process genetic profiles, treatment history, lab values, and clinical guidelines to suggest tailored therapy plans. They predict likely responses to specific drugs or combinations.
This leads to more precise treatment strategies, fewer adverse reactions, and better patient outcomes over time.
24. Surgical robotics & procedure assistance
Robotic systems equipped with vision and motion algorithms guide instruments with high precision. They assist surgeons by stabilizing movements, adjusting tool paths, or providing real-time anatomical overlays.
This increases procedural accuracy, reduces complications, and shortens recovery times, which helps hospitals improve operating room efficiency.
25. Clinical trial optimization & patient matching
Models analyze patient records, genetic data, demographic factors, and trial criteria to identify individuals who meet strict enrollment requirements. They also predict which sites are likely to meet recruitment goals.
This accelerates trial enrollment, reduces costly delays, and increases the likelihood of obtaining meaningful clinical results.
26. AI-powered virtual nursing assistants
These systems answer routine patient questions, monitor symptom updates, and remind patients about medication or appointments. They operate through mobile apps, chat interfaces, or voice systems.
This reduces the load on nursing staff and keeps patients engaged between visits, improving adherence and post-treatment follow-up.
27. Genomics & biomarker discovery
AI models scan genomic sequences, protein structures, and biological datasets to identify markers linked to diseases or treatment response. They find patterns that are hard to detect manually due to data volume and complexity.
This supports targeted drug development and improves diagnostic accuracy in precision medicine programs.
28. Automated administrative workflow & documentation
AI tools handle repetitive tasks such as appointment scheduling, claim preparation, coding suggestions, and form completion. They integrate with EHR systems to extract key data fields automatically.
This reduces administrative strain on clinical staff and lowers the number of documentation errors that affect billing cycles.
29. Natural language processing for clinical note transcription & analysis
Speech recognition and text-processing models convert conversations into structured clinical notes. They also analyze existing notes to extract medical concepts, highlight risk factors, and identify inconsistencies.
This cuts time spent on manual documentation and improves the completeness of patient records, supporting both clinical decisions and billing accuracy.
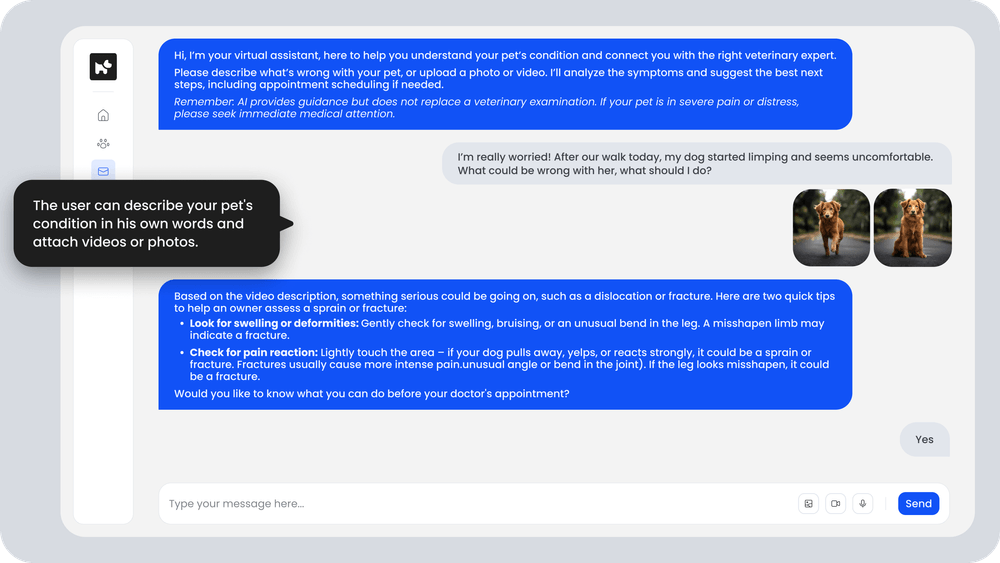
30. Virtual triage assistant for pet owner inquiries
AI chat and voice tools collect symptoms described by pet owners, ask follow-up questions, and classify the urgency of the case. They recommend next steps such as immediate visit, scheduled appointment, or home care instructions.
Clinics use this to reduce unnecessary walk-ins, better manage appointment load, and give owners clear guidance before arrival.
31. Predictive analytics for emergency room triage and resource allocation
AI tools analyze presenting symptoms, vital signs, and historical cases to predict condition severity and likely treatment needs. They suggest priority levels and estimate required resources such as imaging, surgery, or hospitalization.
This helps emergency units reduce wait times, allocate staff efficiently, and improve outcomes for high-risk cases.
32. Automated analysis of lab results (e.g., bloodwork, urinalysis)
Models read lab data and detect abnormal ranges, correlations between biomarkers, and early indicators of infections, organ dysfunction, or metabolic issues. They produce structured summaries for veterinarians.
This speeds up interpretation, lowers the risk of oversight during busy hours, and supports faster treatment decisions.
33. AI co-pilot for clinical note generation & administrative workflow
Speech recognition and text models convert consultations into structured notes with diagnosis details, procedures, medications, and follow-up plans. They also fill common fields in practice management systems.
Thanks to this, clinics can reduce administrative load, shorten appointment wrap-up time, and keep records consistent across veterinarians.
34. Breed-specific early disease detection models
AI systems analyze breed-related risks combined with symptoms, genetic data, and medical history. They detect patterns linked to conditions that occur more frequently in specific breeds, such as cardiac issues, joint disorders, or metabolic diseases.
This supports earlier diagnosis, reduces long-term treatment costs, and enhances preventive care programs offered by clinics.
35. Pain and behavior analysis via video monitoring
Computer vision models track posture, gait, facial expressions, and activity patterns in pets. They compare these signals to known markers of pain, anxiety, or mobility problems.
This offers objective assessment that complements clinical observation, helping veterinarians adjust treatment plans and monitor recovery more accurately.
36. Diagnostic support for dermatological conditions (skin lesions, allergies)
Image-analysis models review photos of skin lesions, rashes, and inflammation. They classify common issues such as fungal infections, parasite-related conditions, or allergic reactions.
Clinics use this to speed up diagnosis, reduce unnecessary lab tests, and provide more consistent treatment recommendations.
Manufacturing
37. Predictive maintenance
Models monitor sensor data from machines such as vibration, temperature, pressure, and power usage. They learn patterns that appear before failures and send alerts when these patterns reoccur.
As a result, manufacturers schedule maintenance before breakdowns, reduce unplanned downtime, and keep production lines stable.
38. Generative design for parts and components
Generative systems take engineering constraints such as load, weight, material type, and safety requirements and produce multiple design options that meet those limits. Engineers then select and refine the most efficient version.
This shortens design cycles and often results in components that use less material, reduce weight, or improve durability.
39. AI-powered visual quality inspection
Computer vision models analyze images or video streams from cameras on the production line. They detect surface defects, assembly errors, missing parts, and improper alignment.
This allows the need for manual inspection and catches issues earlier, which lowers scrap rates and avoids costly rework.
40. Digital twins for process optimization
A digital twin is a virtual model of equipment or a full production line. AI systems simulate different operating conditions, test parameter changes, and predict the impact of adjustments.
Manufacturers use this to optimize throughput, evaluate new settings without interrupting production, and improve decision-making around capacity and scheduling.
41. Yield enhancement and root cause analysis
Models analyze large volumes of production data, including machine parameters, environmental conditions, and operator actions. They identify combinations of factors that reduce yield or trigger defects.
By isolating these causes, manufacturers can adjust processes, improve consistency, and reduce waste across product batches.
42. Robotics process automation (RPA) for back-office manufacturing tasks
RPA tools handle repetitive digital work such as order entry, shipment scheduling, invoice matching, and production reporting. They follow rule-based workflows and integrate with ERP or MES systems.
This reduces manual workload for administrative teams and decreases the number of data-entry errors that can slow down production planning.
43. Generative AI for technical documentation and work instructions
Generative models create drafts of manuals, assembly guides, troubleshooting steps, and safety instructions based on engineering specs and process data. They can also update content automatically after design or workflow changes.
This cuts the effort spent on documentation and helps teams keep instructions consistent and up to date across all production sites.
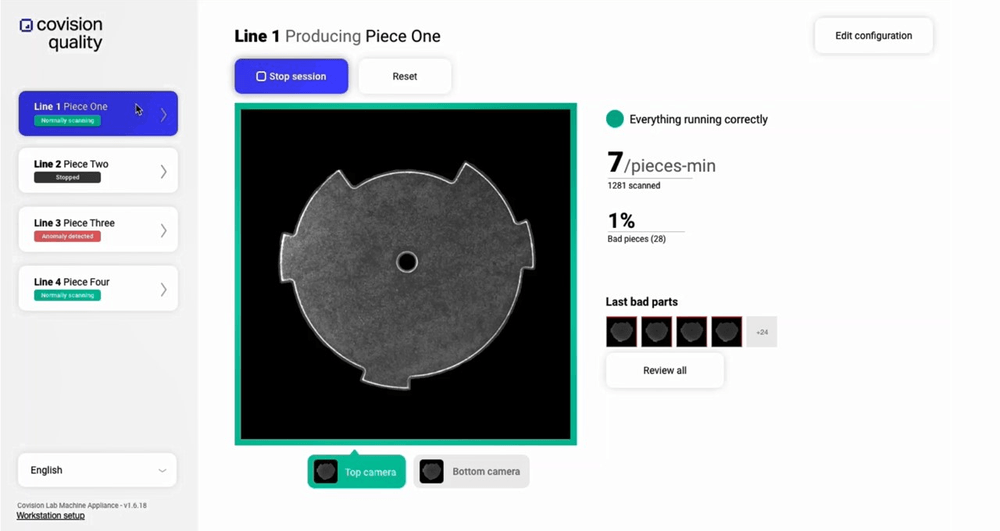
Legal
44. Contract review and analysis
Models scan contracts for clauses, deadlines, risks, missing terms, and unusual language. They compare documents against templates or past agreements and flag sections that need revision.
Law firms and in-house teams speed up review cycles, reduce human error, and maintain consistency across large volumes of documents.
45. eDiscovery and document triage
AI processes emails, files, chats, and archives to identify relevant evidence in litigation or investigations. It clusters documents by topic, labels sensitive material, and removes duplicates.
With AI being a new smart paralegal, legal teams cut review time, reduce billable hours per case, and surface key information sooner in the process.
46. Legal research and precedent retrieval
The system searches statutes, filings, case law, and opinions, then ranks results based on legal relevance instead of keyword matches.
Attorneys reach strong arguments faster, limit time spent on manual research, and avoid missing important precedents.
47. Due diligence automation
AI extracts key facts from financial statements, contracts, compliance reports, and corporate records during M&A or investment checks. It highlights red flags and organizes findings into structured summaries.
Firms process more deals in less time and build a clearer picture of risks before negotiation.
48. Litigation outcome prediction
Models analyze past judgments, judge-specific tendencies, case timelines, claim characteristics, and jurisdiction patterns to estimate probable outcomes.
Lawyers gain data-backed expectations that support strategy planning, settlement evaluation, and resource allocation.
49. Contract lifecycle management
AI tracks renewals, obligations, approvals, and risk markers across contract portfolios. It automates reminders, organizes amendments, and assists with version control.
Organizations reduce missed deadlines, improve compliance with obligations, and maintain cleaner contract workflows.
50. Intellectual property (IP) prior art search
Machine learning reviews patents, academic papers, product descriptions, and technical databases to identify similar inventions.
Companies strengthen their filings, avoid infringement exposure, and shorten the time required for patent research.
51. Compliance monitoring and regulatory change management
The system monitors regulatory updates, extracts relevant parts, and maps them to internal policies or processes.
Regulated industries adapt faster to new requirements and lower the risk of penalties linked to outdated compliance practices.
52. Automated drafting of legal documents
AI creates first drafts of NDAs, employment agreements, policies, motions, and other standard documents based on templates and user inputs.
Teams shift their time from boilerplate writing to higher-value analysis and reduce drafting bottlenecks.
53. AI-powered deposition and transcript analysis
Models process deposition transcripts, hearing notes, or meeting recordings to highlight contradictions, key statements, timelines, and thematic patterns.
Litigators move through long transcripts more efficiently and build clearer narratives for case preparation.
54. Bankruptcy prediction for corporate clients
AI evaluates financial reports, cash-flow trends, credit history, and market signals to flag companies with rising insolvency risk.
Law firms and corporate departments make earlier decisions about restructuring, credit exposure, and contract adjustments.
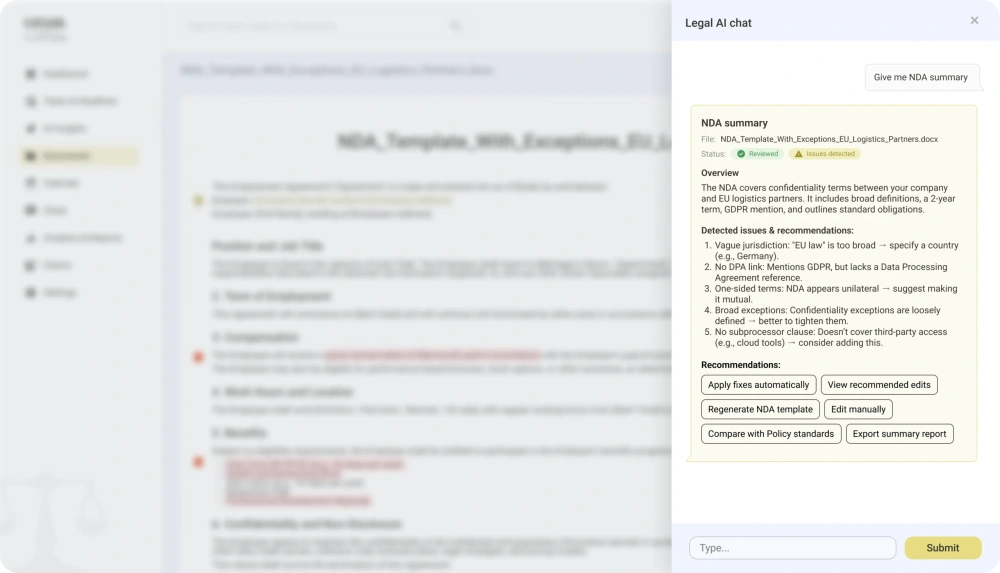
Logistics and transportation
55. Route optimization and delivery planning
AI evaluates traffic patterns, delivery windows, vehicle capacities, and historical delays to build efficient daily routes.
Companies cut fuel costs, tighten delivery times, and reduce bottlenecks caused by manual route adjustments.
56. Predictive maintenance for fleet vehicles
Models process engine data, sensor readings, driver behavior logs, and repair history to predict breakdowns before they occur.
Fleet managers avoid unplanned downtime, reduce repair expenses, and keep vehicles available during high-demand periods.
57. Warehouse automation and robotics
Computer vision guides robots for picking, sorting, palletizing, and shelf replenishment. The system assigns tasks based on order priority and current warehouse load.
Operations move faster, picking accuracy improves, and staffing pressure decreases during seasonal spikes.
58. Demand forecasting and capacity planning
AI reviews order data, seasonal patterns, pricing changes, and external variables like weather or promotions to predict shipment volumes.
Carriers plan workforce needs in advance, secure enough vehicles, and avoid overbooking or underutilized assets.
59. Real-time shipment tracking and ETA prediction
Models combine GPS data, road conditions, driver behavior, and historical delays to produce accurate arrival estimates.
Shippers reduce customer inquiries, improve transparency, and correct delivery issues before they escalate.
60. Fraud detection in shipping and claims
AI scans claims, package images, shipment logs, and customer behavior for inconsistent patterns that signal false reports or manipulated paperwork.
Fraud losses shrink, investigations speed up, and legitimate claims move through the system more smoothly.
61. Driver safety monitoring and behavior analysis
Camera systems and sensors monitor lane drifting, fatigue signals, harsh braking, and speeding. AI highlights risky patterns and generates safety reports.
Insurance costs decrease, accident rates drop, and drivers receive clearer guidance for safer habits.
62. Automated dock scheduling and yard management
The system analyzes incoming loads, vehicle arrival times, and dock availability to assign optimal slots. Yard cameras track trailer locations and loading status.
Facilities shorten waiting lines, improve throughput, and maintain steadier workflows.
63. Dynamic freight pricing
AI evaluates demand levels, fuel prices, lane capacity, competitor activity, and historical margins to recommend fair and profitable rates.
Carriers secure better margins and avoid price decisions based solely on manual market scans.
64. Last-mile delivery optimization with autonomous vehicles or drones
Autonomous units rely on navigation models and route planning algorithms to deliver small parcels under predictable conditions.
Retailers and carriers lower delivery costs in dense zones, reduce driver load, and expand same-day delivery coverage.
Real estate
65. Automated lease abstraction and document analysis
This solution scans lease agreements, extracts key terms, and organizes them into structured fields. It uses OCR and language models trained on real estate contracts to recognize clauses, dates, responsibilities, and financial terms.
This reduces manual review time, cuts the risk of missed obligations, and speeds up onboarding of new assets.
66. AI-powered property valuation and comparative market analysis (CMA)
This system estimates a property’s value by reviewing listings, past sales, neighborhood records, and price trends. It applies regression models and pattern-finding methods to match a property with similar ones in the area.
It gives more consistent valuations, supports quicker decision-making, and improves pricing accuracy for listings and acquisitions.
67. Virtual staging and interior design rendering
AI creates staged rooms or full interiors from empty photos or floor plans. It generates furniture layouts, décor options, and multiple style choices with minimal human effort.
Thanks to this, listings can stand out online, boost buyer interest, and cut the cost and time of physical staging.
68. Predictive maintenance for building systems and major components
Sensors and maintenance logs feed an AI model that forecasts when HVAC units, elevators, pumps, or other equipment may fail. The system looks at usage patterns, temperature, vibration, and repair history.
It extends equipment lifespan, lowers emergency repair costs, and improves tenant satisfaction through fewer disruptions.
69. Tenant risk assessment and rental application scoring
This solution reviews credit indicators, rental history, digital footprints, and income stability to predict the chance of late payments or early move-outs.
As a result, property managers choose applicants with lower financial risk and reduce default-related loss.
70. AI for commercial property utilization and space optimization
Sensors, badge data, and booking systems provide usage information. AI detects occupancy trends, unused rooms, and traffic patterns across floors or buildings.
It supports better space planning, reduces wasted square footage, and helps owners adjust layouts or leasing strategies.
71. Generative AI for architectural plans and renovation designs
This system produces draft layouts, room adjustments, design options, or renovation concepts from requirements or existing building data. It can sketch variations quickly and adapt designs based on constraints.
It shortens early design cycles, helps clients visualize ideas faster, and lowers planning costs.
72. AI-driven construction site monitoring and progress analysis
Cameras, drones, and sensor streams are processed by computer vision models that track work progress, detect hazards, and compare real conditions with schedules.
This increases project transparency, reduces delays, and supports faster response to safety issues or bottlenecks.
73. Predictive analytics for neighborhood investment and “hot spot” identification
Market data, migration trends, local business activity, school ratings, and public records feed a model that flags areas likely to grow in price or rental demand.
It supports smarter investment planning and early entry into markets with strong potential.
74. Client interactions and communication
AI helps agents answer buyer questions, craft emails, prepare listing summaries, and keep track of client preferences. It uses conversation history and property data to recommend replies and produce consistent communication.
It saves time, speeds up lead response, and improves the overall client experience.
Agriculture & food production
75. Food quality sorting and defect detection on processing lines
Computer vision systems inspect fruits, vegetables, grains, and packaged goods as they move along conveyors. The model detects size issues, bruises, mold, foreign objects, and other defects in real time.
This improves product consistency, cuts waste, and reduces labor costs tied to manual sorting.
76. Predictive yield forecasting and harvest planning
Models process satellite data, drone imagery, soil readings, and weather patterns to estimate crop performance weeks or months in advance.
Thanks to this, farmers plan labor, transport, and storage needs more accurately, which reduces last-minute expenses and supports better pricing decisions.
77. Precision fertilization & chemical application
Sensors and field maps are combined with AI models to determine the right amount of fertilizer or crop protection for each field zone. Application equipment then adjusts dosage accordingly.
This cuts chemical costs, improves plant health, and reduces environmental impact.
78. AI-optimized irrigation and water management
Moisture sensors, weather data, and crop growth models allow the system to decide when and how much water to apply.
It helps reduce water waste, lowers utility expenses, and protects crops from overwatering or drought stress.
79. Automated weed & pest identification and spot-spraying
Camera-equipped tractors or drones scan fields and detect weeds or pest activity. The sprayer then applies treatment only where needed.
This cuts chemical usage, saves money, and reduces crop damage caused by late detection.
80. Predictive analytics for crop disease outbreaks
Satellite imagery, humidity levels, historical outbreaks, and temperature patterns are combined to highlight areas at risk of disease spread.
It helps farmers act sooner, protect affected zones, and avoid large-scale crop loss.
81. Soil health analysis and nutrient deficiency detection
AI reviews soil samples, lab data, and field images to spot nutrient gaps, pH issues, compaction zones, or moisture problems.
This supports better fertilization plans, stronger crop growth, and higher yield stability.
82. Supply chain & spoilage prediction for perishable goods
Temperature logs, transport routes, humidity data, and shipping times feed a model that predicts spoilage risk across the cold chain.
It helps producers and distributors reduce waste, optimize routes, and maintain product quality.
83. Livestock health monitoring via computer vision
Cameras in barns track movement, feeding behavior, posture, and signs of illness. The model alerts staff when animals show patterns linked to stress or disease.
This improves animal welfare, reduces vet costs, and minimizes productivity loss.
84. Autonomous harvesting and selective picking
Robotic harvesters use vision models to detect ripe produce and pick it without damaging the crop.
This reduces reliance on seasonal labor and supports consistent harvesting during peak periods, though the technology is still limited to certain crop types.

Energy (oil&gas, renewable energy, utilities)
85. Predictive maintenance for infrastructure (e.g., turbines, pipelines, substations)
Sensor data from vibration, temperature, pressure, and acoustic monitors is analyzed to flag equipment that is likely to fail. Models detect patterns linked to early wear, corrosion, or abnormal behavior.
This reduces downtime, cuts repair costs, increases asset lifespan, and lowers the risk of safety incidents.
86. Smart grid management & load forecasting
Demand data, weather patterns, and historical usage help models predict electricity peaks and adjust load distribution. Utilities use this to reroute power, balance the grid, and prevent overloads.
It improves service stability, reduces blackout risk, and helps operators match generation with real demand.
87. Renewable energy forecasting (solar and wind output)
Weather forecasts, cloud movements, wind speed maps, irradiance data, and turbine behavior feed prediction models that estimate upcoming generation capacity.
This helps utilities schedule backup supply more accurately, avoid overproduction, and improve grid planning.
88. Energy consumption optimization for utilities and consumers
Models study usage patterns in homes, factories, and city systems to recommend ways to cut waste or shift load to cheaper hours.
It lowers operating costs, helps customers save money, and supports more efficient grid usage.
89. Autonomous inspection via drones and robotics
Drones equipped with cameras, infrared sensors, and gas detectors inspect pipelines, refineries, offshore rigs, and wind turbines. AI flags cracks, leaks, corrosion, vegetation encroachment, or
structural issues.
This cuts manual inspection costs, reduces safety risks, and speeds up reporting.
90. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for field data capture
RPA bots pull data from SCADA logs, maintenance reports, and field notes, then convert it into structured formats for dashboards and audits.
This reduces administrative workload, shortens reporting cycles, and improves data accuracy.
91. AI-powered carbon emissions tracking and management
Models gather emissions data from equipment, sensors, and fuel records, then calculate CO₂ output and detect areas with unusually high emissions.
Companies can reduce compliance penalties, improve reporting accuracy, and plan reduction initiatives more effectively.
92. Reservoir analysis and hydrocarbon recovery optimization (O&G)
AI reviews seismic data, pressure readings, flow rates, and rock properties to estimate reservoir performance. It suggests ideal injection strategies and well spacing.
This leads to better recovery rates, fewer drilling mistakes, and improved well productivity.
93. AI for drilling optimization and real-time anomaly detection (O&G)
During drilling, models monitor torque, mud flow, pressure, and vibrations to detect kicks, stuck pipe risks, or unstable formations. They also help select better drilling parameters.
This reduces non-productive time, prevents equipment damage, and improves drilling speed.
94. AI-enhanced seismic interpretation (O&G)
Computer vision models analyze seismic volumes to detect faults, traps, and structural patterns faster than manual interpretation.
It shortens exploration timelines, improves accuracy, and reduces the risk of drilling dry wells.
95. Dynamic energy trading and price optimization
Trading systems use market data, weather trends, supply-demand shifts, and historical prices to suggest when to buy or sell energy.
Thanks to this, traders reduce risk, secure better margins, and react faster to market swings.
96. Automated geospatial analysis for renewable site selection
Satellite imagery, land maps, zoning constraints, and environmental data feed models that identify suitable sites for solar farms, wind farms, or geothermal projects.
This reduces early-stage planning time, avoids regulatory issues, and improves long-term project viability.
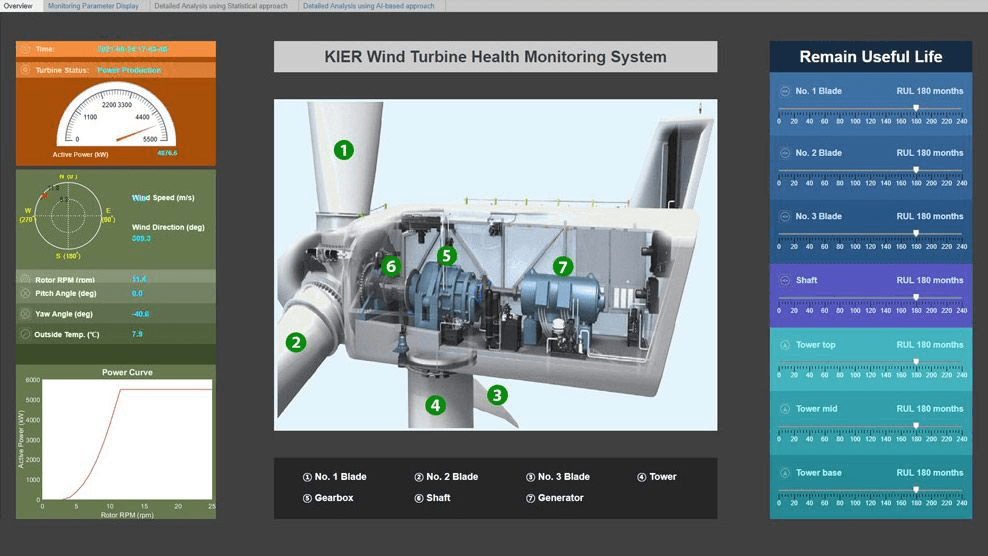
Telecommunications
97. Network optimization and traffic management
AI analyzes traffic flows, bandwidth usage, and signal quality to adjust routing and balance loads across the network.
Operators improve connection stability, reduce congestion incidents, and deliver more consistent service during peak times.
98. Predictive maintenance for infrastructure
Sensor data from towers, fiber equipment, and switches is processed to detect early signs of component failure.
Maintenance teams fix issues before outages occur, which reduces service interruptions and lowers emergency repair costs.
99. Customer churn prediction
AI reviews usage patterns, complaints, billing history, plan changes, and network experience to identify customers at risk of leaving.
Retention teams target the right users with relevant offers and reduce revenue loss from preventable churn.
100. Fraud detection (SIM swap, account takeover, billing fraud)
Models monitor unusual login attempts, rapid SIM changes, irregular billing spikes, and suspicious device activity.
Fraud cases are caught earlier, financial exposure decreases, and customer trust stays intact.
101. Automated field service dispatch and scheduling
AI evaluates technician skills, spare parts availability, urgency levels, and geographic routes to assign field tasks.
Technicians complete more jobs per day, travel time is reduced, and service appointments become easier to predict.
102. Network anomaly detection and security
The system analyzes packets, logs, and user behavior to detect unusual activity that may signal breaches, malware, or misconfigurations.
Security teams respond faster, reduce incident scope, and keep networks compliant with regulatory requirements.
103. Predictive analytics for capacity planning
AI tracks subscriber growth, device types, usage patterns, and regional demand to forecast where capacity upgrades will be required.
Operators invest in network expansion more accurately and avoid slowdowns caused by late infrastructure upgrades.
How much would it cost to build AI solutions like these?
Use our free online cost calculator to learn the price.
Finance
104. Algorithmic trading and execution
Models process market data, order books, price movements, and liquidity signals in real time. They detect patterns that match predefined strategies and place orders automatically when conditions fit those rules.
This reduces manual reaction time, avoids missed opportunities, and helps traders execute orders at more stable prices during fast market shifts.
105. Anti-money laundering (AML) and fraud pattern detection
AI systems analyze transaction flows, account behavior, network connections between entities, and unusual movement patterns. They compare these signals to known risk profiles and detect anomalies that indicate layering, structuring, or suspicious transfers.
This reduces false alerts and allows compliance teams to focus on genuinely high-risk activity, improving both speed and accuracy of investigations.
106. Algorithmic credit underwriting and risk scoring
Models assess creditworthiness by analyzing repayment history, transaction data, spending habits, income stability, and other financial indicators. They detect early signs of risk that rule-based scoring may miss.
Thanks to this, lenders can issue decisions faster, reduce default rates, and expand access to borrowers who fit the profile but lack traditional credit footprints.
107. Regulatory compliance (RegTech) and automated reporting
AI tools extract required fields from contracts, customer files, trade records, or KYC documents. They check data quality, flag missing entries, and create structured reports for regulators.
This cuts manual data processing and reduces reporting errors, which helps financial institutions meet deadlines and avoid compliance breaches.
108. Generative AI for personalized wealth management proposals
Generative models create investment summaries, portfolio explanations, and scenario analyses based on a client’s goals, risk tolerance, income structure, and time horizon. They do this by combining structured financial data with language models trained to generate clear, compliant text.
Advisors use these proposals to prepare client meetings faster and maintain consistent quality across thousands of portfolios.
109. Claims automation and fraud detection in insurance
AI processes claims by extracting data from photos, documents, or messages and matching them to policy rules. Fraud-focused models detect inconsistencies in damage descriptions, repair estimates, claim frequency, and claimant behavior.
This shortens claim cycles for customers and helps insurers reduce payouts linked to fabricated or exaggerated cases.
110. Sentiment analysis for market and news impact trading
Models review news headlines, earnings reports, analyst notes, and social media to classify sentiment and detect events that may influence asset prices. They score each text piece and send signals to trading systems or risk teams.
This gives traders a faster view of market mood, helping them adjust positions before price swings become visible in the charts.
111. Dynamic pricing for insurance premiums
Pricing models evaluate driver behavior, property data, health indicators, claim history, and exposure levels. They update premiums based on real risk rather than broad demographic groups.
Thanks to this, insurers can keep premiums fair for low-risk customers and reduce losses from underpriced high-risk segments.
112. Automated financial document analysis
AI reads financial statements, loan files, contracts, and regulatory forms. It extracts key fields, validates figures across documents, and highlights inconsistencies or missing data.
This cuts the time analysts spend on manual review and improves accuracy during audits, underwriting, or risk assessments.
Media & entertainment
113. Content recommendation engines
Recommendation systems analyze viewing history, watch time, ratings, pause points, search behavior, and user demographics. They match content attributes with individual preferences and generate personalized suggestions across homepages, autoplay queues, and email campaigns.
This increases viewing time, reduces churn, and helps platforms surface their full catalog instead of relying only on popular titles.
114. Automated content moderation
AI models scan text, images, video, and audio uploads to detect policy violations such as hate speech, graphic violence, sexual content, spam, or copyright infringement. They flag or remove content in real time and prioritize cases for human review.
Thanks to this, platforms can scale moderation across billions of posts, maintain community standards, and reduce exposure to harmful content before it spreads.
115. Personalized advertising and ad placement optimization
Models process user behavior, content context, engagement patterns, and advertiser goals to select which ads to show, when to display them, and at what frequency. They also optimize ad load to balance revenue with user experience.
This increases ad revenue per user, improves conversion rates for advertisers, and reduces viewer frustration from irrelevant or excessive ads.
116. Audience analytics and engagement tracking
AI systems aggregate watch patterns, drop-off points, replay behavior, social media reactions, and demographic data. They identify which scenes drive engagement, which content types perform best, and where audiences lose interest.
This supports better content investment decisions, helps creators understand what works, and guides marketing teams toward high-performing assets.
117. Automated subtitle generation and translation
Speech recognition models convert audio into text, then translation systems adapt subtitles into multiple languages. They handle accents, background noise, overlapping dialogue, and context-specific terminology.
This cuts localization costs, speeds up global releases, and makes content accessible to deaf or hard-of-hearing audiences and international viewers.
118. Content metadata tagging and cataloging
Computer vision and language models watch videos or scan scripts to extract actors, objects, scenes, genres, moods, themes, and plot points. They create searchable metadata that organizes libraries and powers discovery features.
This reduces manual tagging work, improves search accuracy, and helps platforms build better recommendation and browsing experiences.
119. Video editing assistance and highlights generation
AI reviews footage to detect key moments such as goals, dramatic scenes, applause, or emotional peaks. It can create short clips, generate highlight reels, or suggest edit points based on pacing and narrative flow.
This shortens post-production time for sports broadcasts, news segments, and social media content, allowing teams to publish faster during live events.
120. Sentiment analysis for reviews and social media
Models classify user reviews, comments, tweets, and forum posts by sentiment and topic. They track how audiences react to releases, detect emerging complaints, and measure brand perception over time.
This helps marketing and product teams respond to issues quickly, adjust campaigns, and identify what audiences appreciate or dislike about specific content.
Bonus list: five AI use cases ANY business can apply today
If none of the previous applications align with your current project, there are still AI applications that work in almost any environment. These cases focus on tasks every organization manages: documentation, reporting, internal communication, process control, and decision support.
121. Intelligent document processing and data extraction
AI reads contracts, invoices, certificates, onboarding forms, scanned PDFs, and emails, then extracts structured fields such as dates, names, amounts, obligations, or product details. Large volumes of mixed-format documents can be processed without manual retyping.
Companies reduce administrative load, speed up back-office operations, and achieve more consistent data quality across internal systems.
122. Automated reporting and business intelligence dashboards
Models gather data from ERP, CRM, finance tools, logistics systems, or analytics platforms, then turn it into structured daily or weekly reports. They also generate short explanations about sudden changes, anomalies, or new trends detected in the data.
Organizations get reliable reporting with fewer delays, managers receive clearer context around performance shifts, and dashboards update without manual intervention.
123. Internal knowledge search and Q&A
AI models index internal databases such as policies, project archives, product instructions, meeting notes, and knowledge bases. Employees can ask questions in natural language, and the system retrieves the exact paragraph or creates a concise, verified answer.
Teams spend less time searching for information, onboarding becomes smoother, and cross-department communication relies less on guesswork. Productivity increases because employees can access correct information at the moment they need it.
124. Workflow automation for routine multi-step tasks
AI triggers and coordinates actions across tools: creating tickets, preparing summaries, updating CRM fields, drafting follow-up emails, populating templates, or routing items for approval. The system chains these steps based on rules, context, or natural-language instructions.
This helps organizations shorten operational cycles, reduce manual errors, and avoid delays tied to repetitive administrative work.
125. AI-driven forecasting for general operations and staffing
Models analyze historical activity patterns, seasonality, customer inflow, internal workload, and external signals to forecast demand for staff hours, support volume, procurement needs, or operational peaks.
Thanks to this, management teams plan resources more accurately, avoid overstaffing or understaffing, and prepare for workload spikes before they occur.